Z-filter MQ-MAS
Amoureux and coworkers introduced the z-filter approach to MQMAS experiment. It symmetrizes the coherence transfer pathways of both echo and anti-echo signals.
It acquires the echo and anti-echo signals with the same intensity. Therefore, z-filter approach is an amplitude-modulated sequence, which provides us with a pure absorption 2D lineshape.
The delay tau is of order of few microseconds. The third pulse is a selective pi/2 pulse for the central transition.
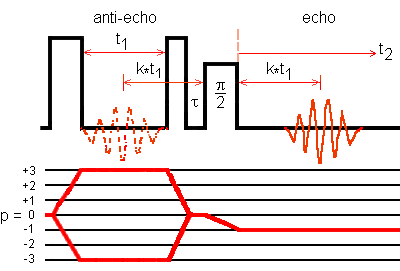
The echo amplitude and the antiecho amplitude have the same sign.
For a spin I = 3/2 and 3QMAS experiment,
0Q -> +3Q -> +0Q -> -1Q is the anti-echo pathway,
0Q -> -3Q -> +0Q -> -1Q is the echo pathway.
For the other half-integer spins and 3QMAS experiment,
0Q -> +3Q -> +0Q -> -1Q is the echo pathway,
0Q -> -3Q -> +0Q -> -1Q is the anti-echo pathway.
ACQUISITION: Hyper-complex or TPPI
Shearing transformation is required to obtain 2D isotropic (in F1 dimension) anisotropic (in the F2 dimension) correlation spectrum.