Modulated Radio Frequency MQ-MAS
Vosegaard and coworkers investigated several MQMAS sequences involving modulated RF pulses, which are also called FAM(I) pulses.
FAM(I) sequence involves a train of equally spaced pulses of equal duration and alternating phases of 0 and pi (denoted x and x bar).
The idea behind the x and x bar pulse trains derives from the cosine amplitude modulated mixing period proposed by Vega and Naor for 3Q to 1Q conversion in single crystals of spin-3/2 systems. It relies on selective irradiation on the satellite transitions.
One important property of FAM pulses is that they are selective for delta p = ±2 coherence order changes and have little beneficial effect upon either the p = +3 to -1 (delta p = -4) conversion or the p = ±3 to 0 (delta p = ±3) conversion.
First sequence
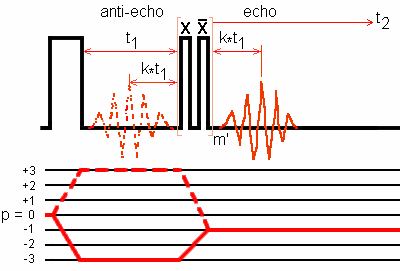
For I = 3/2, modulated pulses mainly transfer the echo pathway signal. This selectivity has the drawback that it inhibits the acquisition of the anti-echo pathway signal which is necessary in the hypercomplex or TPPI approaches to pure absorption lineshapes.
Some distortions of the lineshapes are observed, showing that this sequence does not provide a pure absorption spectrum.
Second sequence
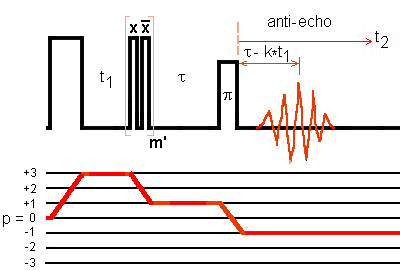
For spin I = 3/2 nuclei, only the p = 0 -> +3 -> +1Q -> -1Q pathway signal is refocused at positive t2 values. Therefore in shifted-echo experiment, the anti-echo shifts towards lower t2 values with increasing t1.
Third sequence
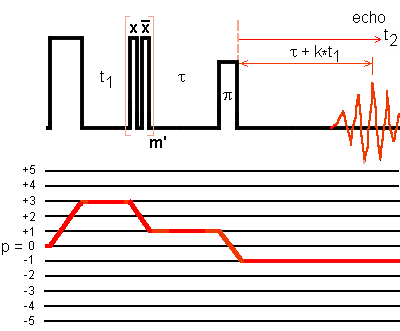
This figure represents the 3Q-MAS with the shifted echo approach and FAM for conversion pulse, applied to a spin I = 5/2.
For 3Q MAS with I = 5/2, most of the observed NMR signal (90%) resulted from the echo pathway; hence phase modulated sequence is sufficient.
The sensitivity is approximately doubled compared to the single-pulse mixing sequence.
This approach provides us with a pure absorption 2D lineshape.
ACQUISITION: F1-QF
Shearing transformation is avoided.
Fourth sequence
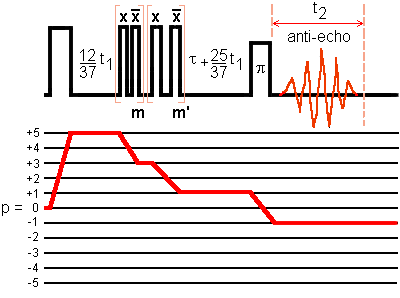
This figure represents the 5Q-MAS with the shifted echo approach and FAM for conversion pulse, applied to a spin I = 5/2.
The first pulse trains have a fixed modulation frequency tuned near the singularity of the outer satellite transitions.
The second pulse trains have a fixed modulation frequency tuned near the singularity of the inner satellite transitions.
The sensitivity is approximately doubled compared to the single-pulse mixing sequence.
This approach provides us with a pure absorption 2D lineshape.
ACQUISITION: F1-QF
Shearing transformation is avoided.
