We may use MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE for our C/C++ projects.
As an example, we present a C mymath project that generates the shared library mymath.dll.
The later is called by a C executable example project. These two projects
are provided by Elias Volanakis
We also present the procedure for obtaining our 64-bit shared library svdComplexDevice1.dll with
MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE for Java developers.
*** Outline ***
- MinGW installation
- PATH variable editing for MinGW
- The C shared library mymath project with MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE
- The C executable example project calling mymath.dll
with MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE
- The C++ 64-bit shared library svdComplexDevice1.dll project with MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE
- Various references
MinGW installation
Semicolon: How to fix MinGW file downloaded incorrectly error
- Download
winlibs-x86_64-posix-seh-gcc-14.2.0-mingw-w64msvcrt-12.0.0-r2.zip: GCC 14.2.0 (with POSIX threads)
+ MinGW-w64 12.0.0 (MSVCRT) - release 2 without LLVM/Clang/LLD/LLDB for 64 bit Windows.
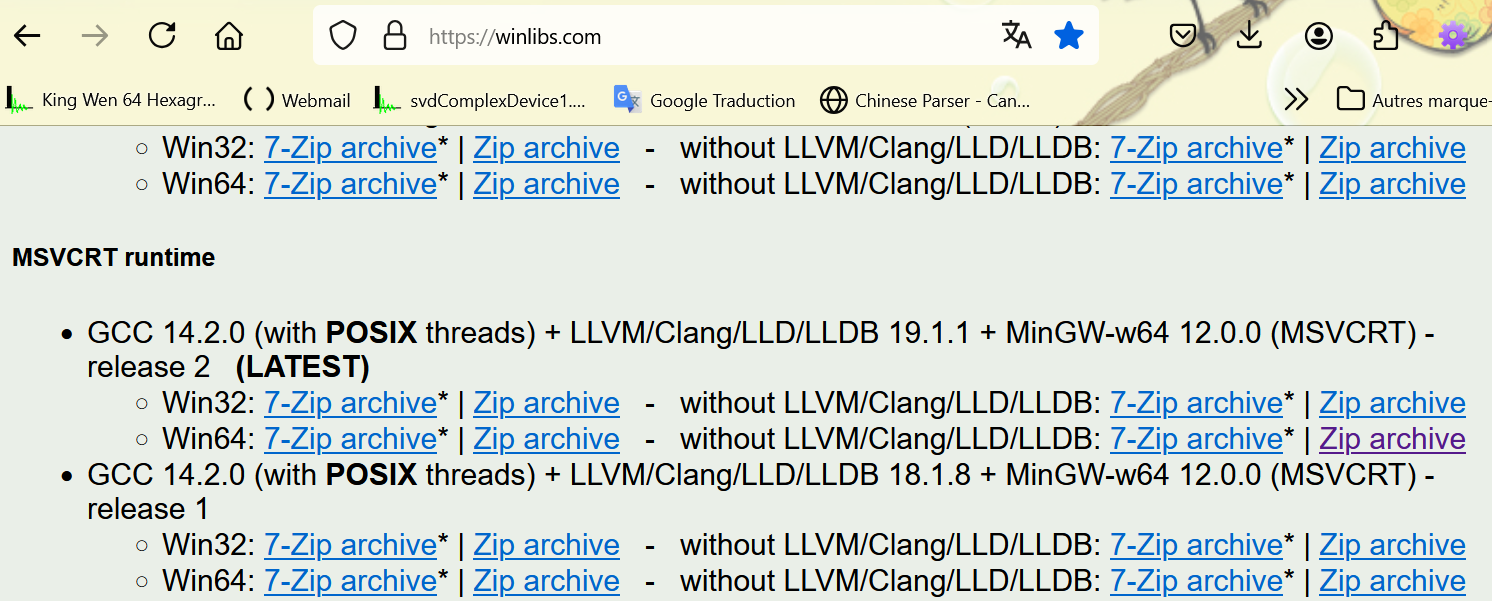
- Create an empty folder mingwu on C disk, for example C:\mingw
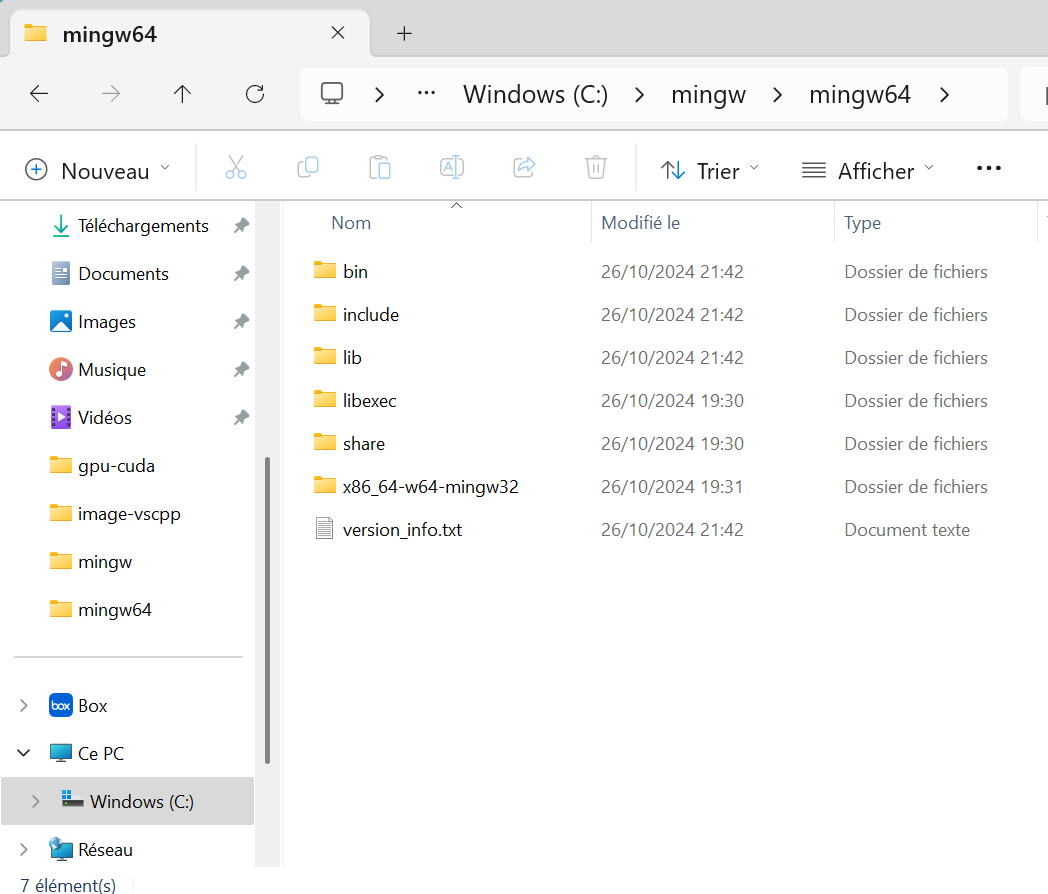
- Unzip mingw64 file into C:\mingw
- After installation, the folder contains:
PATH variable editing for MinGW
After installing MinGW, edit PATH variable of Windows 11.
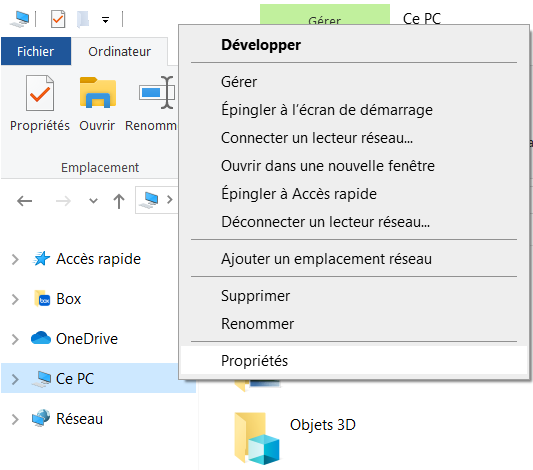
- Right click PC computer then select Properties.
- System panel appears.
Select Advanced system parameters.
System properties panel appears.
Click Environment Variables... button. - Environment variables panel appears.
Select Path in System variable box.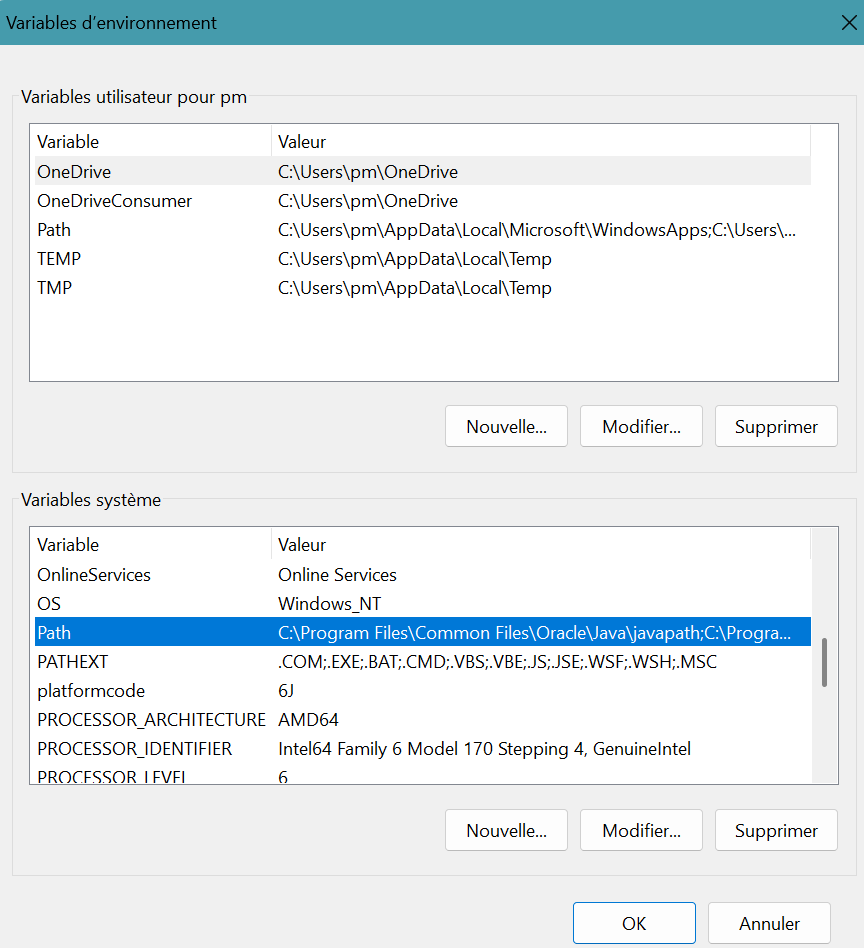
- Click Edit... button.
Click Modify... button.
Click New button.
Add C:\mingw\mingw64\binClick OK buttons.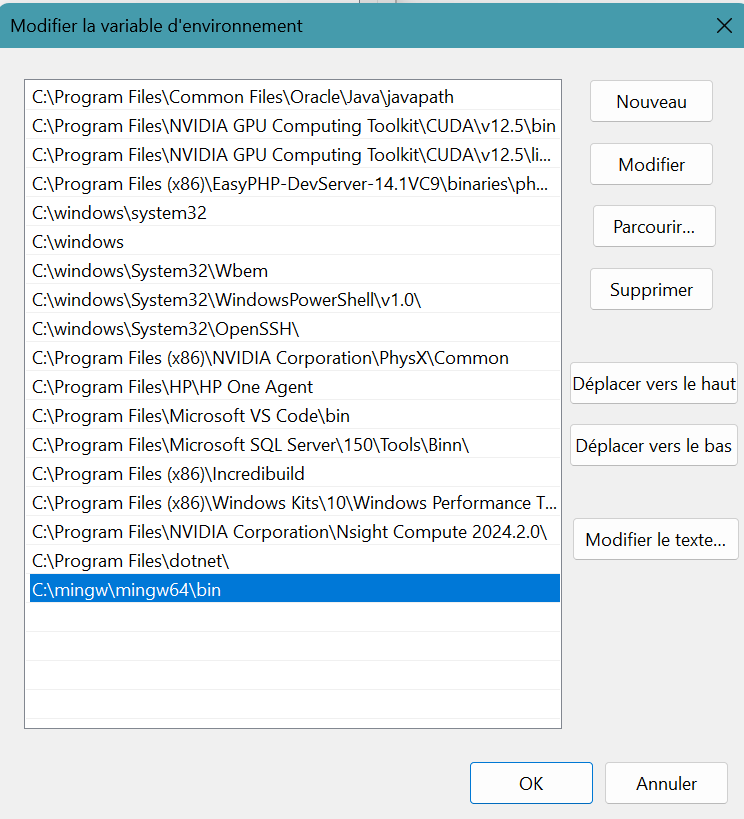
- Test the installation:
Enter cmd in Search of Windows.
The command prompt of Windows appears.
Enter g++ --version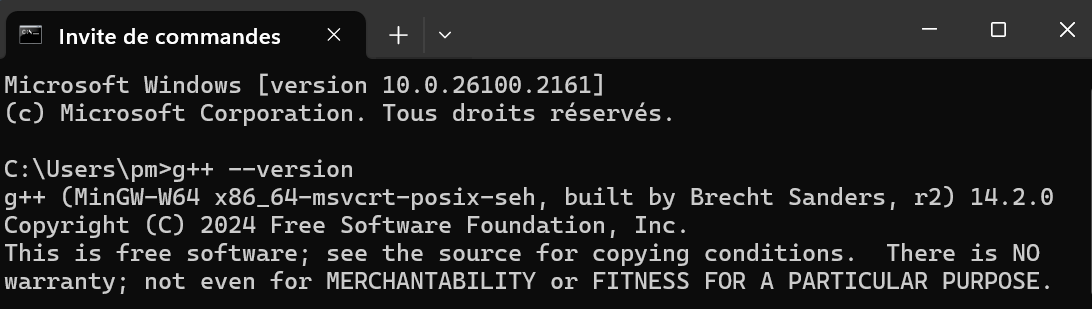
C shared library mymath project with MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE
- Launch Eclipse IDE for Java Developers.
Select File, New, Project...

New Project panel appears.
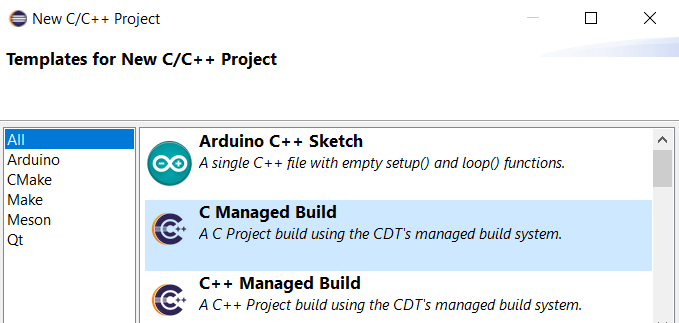
Select C/C++ Project.
Click New > button. - New C/C++ Project panel appears.
Select C Managed Build.Click Next > button. - C Project panel appears.
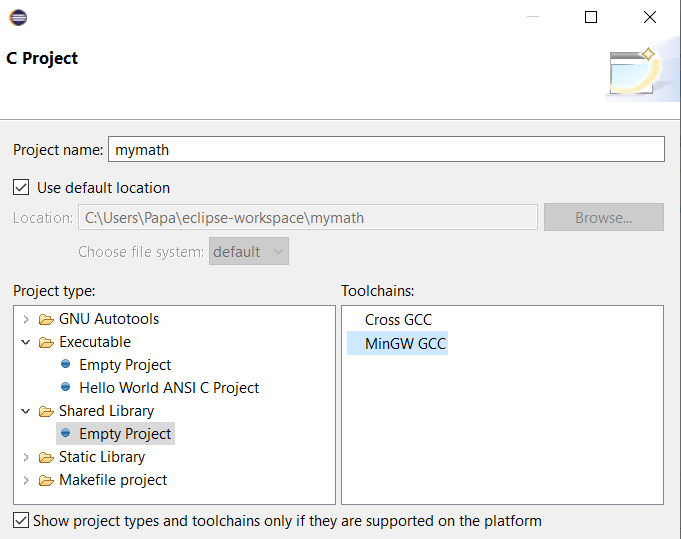
Provide Project name: mymath
Select Shared Library then Empty Project.
Select MinGW GCC in Toolchains.Click Finish button. - The project folder mymath appears in Package Explorer of Eclipse.
- Click File menu. Select New, then File.
Create New File panel appears.
Provid File Name: mymath.hClick Finish button.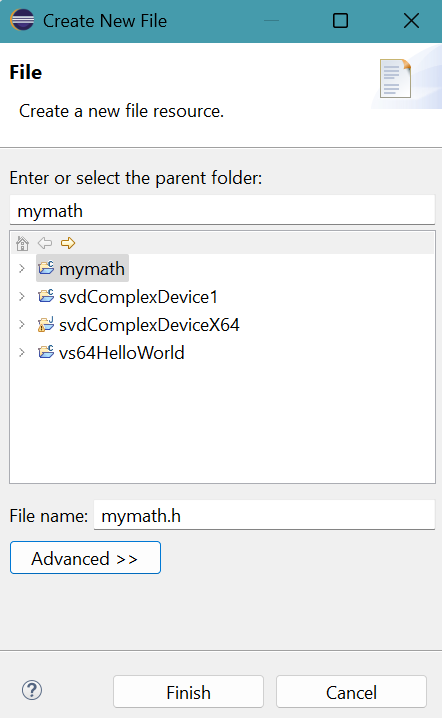
- An empty file mymath.h appears in mymath folder.
Copy and past mymath.h file into the newly created header file.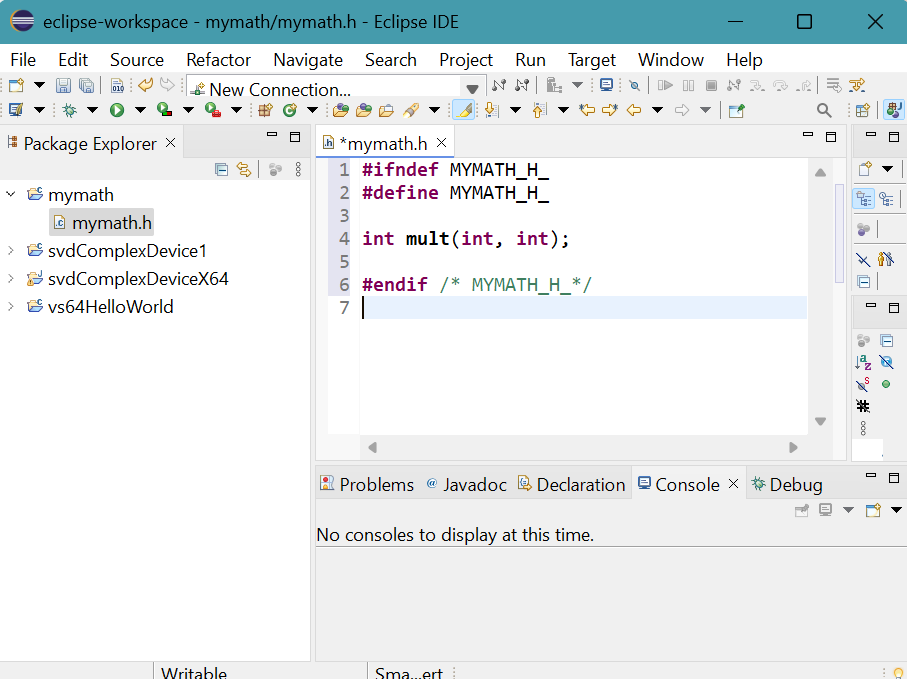
- Similarly, create the folder mymath.c in Package Explorer of Eclipse.
- Copy and past mymath.c file into the newly created source file.
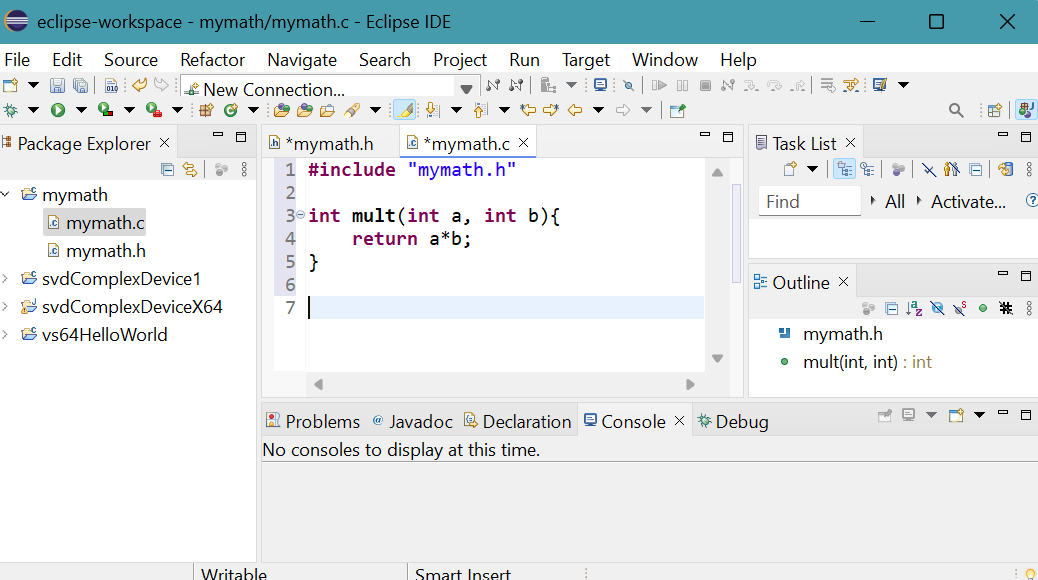
- To delete the first three letters lib in libmymath.dll,
right click the project name in Package Explorer.
Select Properties...
Properties for mymath panel appears.
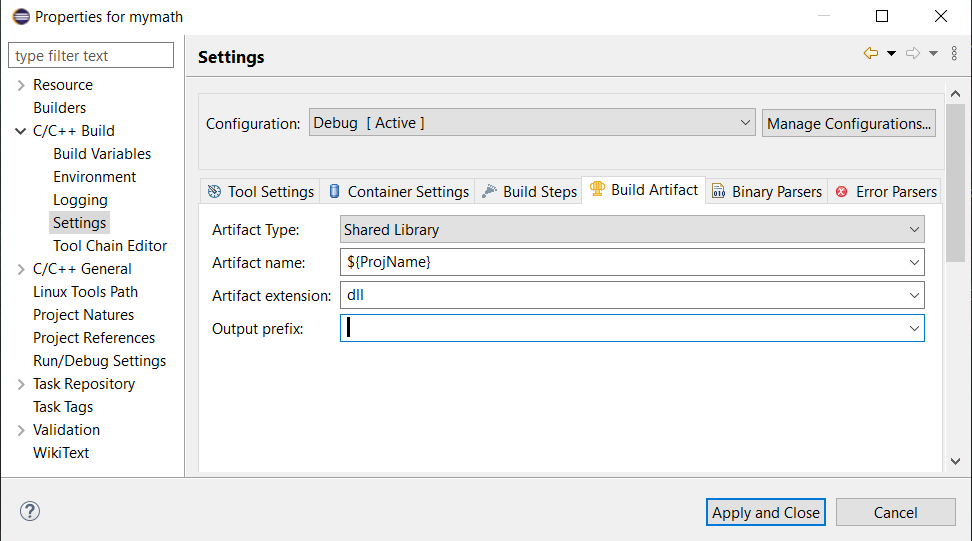
Click C/C++ Build then Settings.
Click Build Artifact tab.
Select Shared Library for Artifact Type.
Delete lib in Output prefix.Click Apply and Close button. - Select Project menu then Build All.
A folder, Debug, appears in Package Explorer. It contains the 64-bit DLL file mymath.dll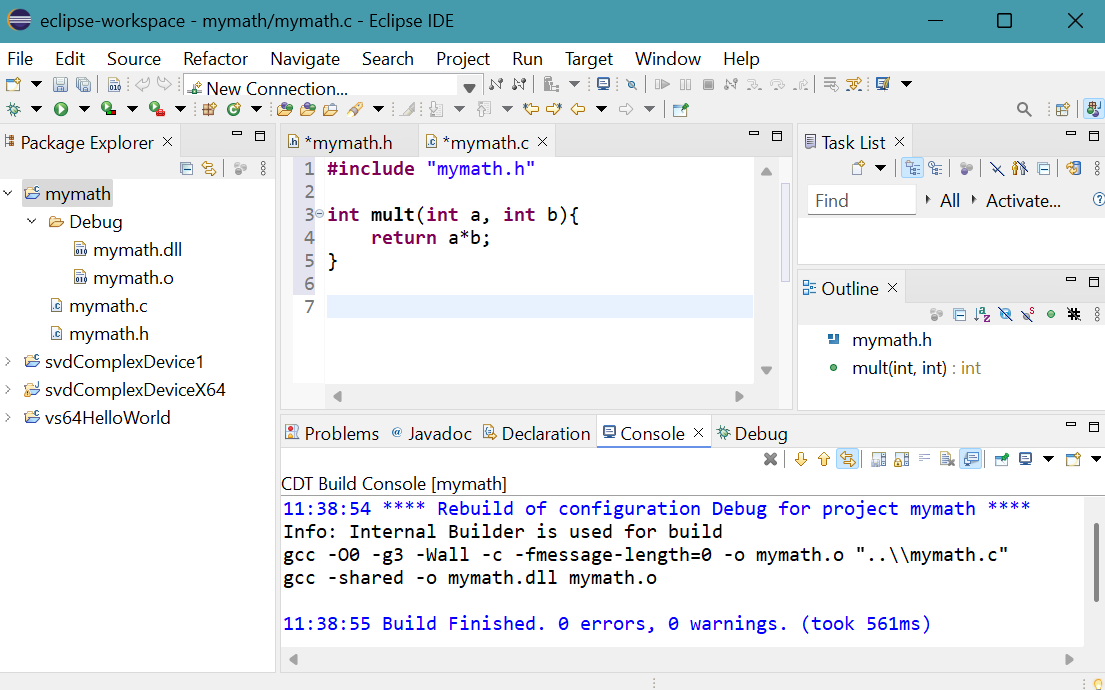
C executable example project calling mymath.dll with MinGW GCC toolchain in Eclipse IDE
We must specify three data during the setup of this project:
(1) the path of header file mymath.h to the compiler,
(2) the shared library mymath.dll and the path of its folder to the linker,
(3) the folder path of shared library mymath.dll to operating system Windows 11.
- Click File Menu of Eclipse. Select New, then Project...
New project panel appears.
Select C/C++ Project.
Click Next > button.
New C/C++ Project panel appears.
Select C Managed Build.
Click Next > button.
C Project panel appears.
Select Empty Project for Executable.
Select MinGW GCC for Toolchains.
Provide the project name: exampleClick Finish button.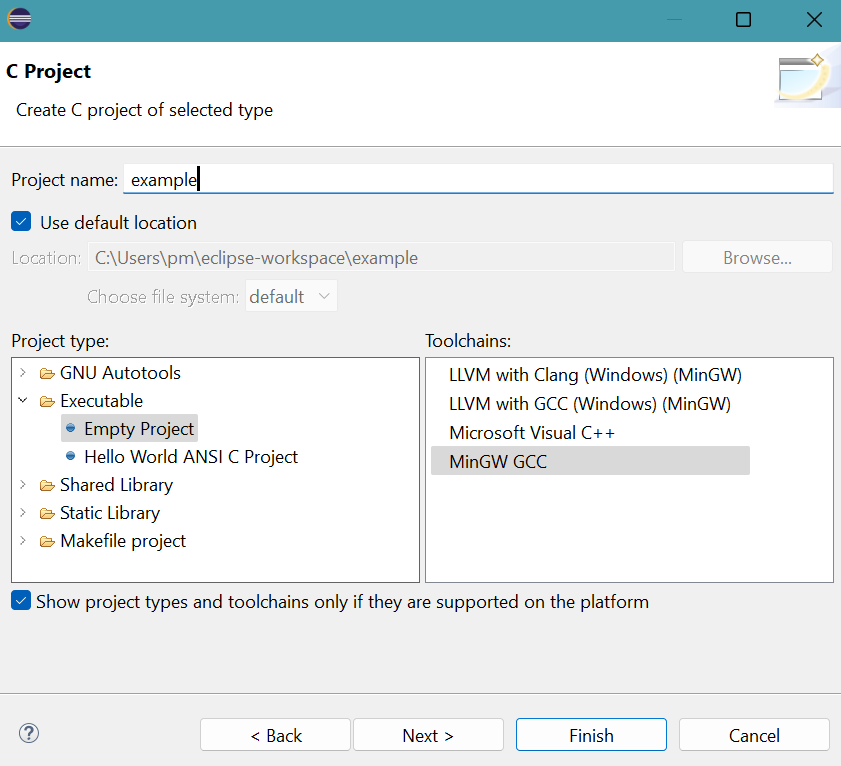
- Right click example project in Package Explorer, then New, finally File.
Create New File panel appears. Provide the File name: example.c
Click Finish button. - Copy example.c and paste it into the newly generated file.
#include "mymath.h" is wavy underlined in red.
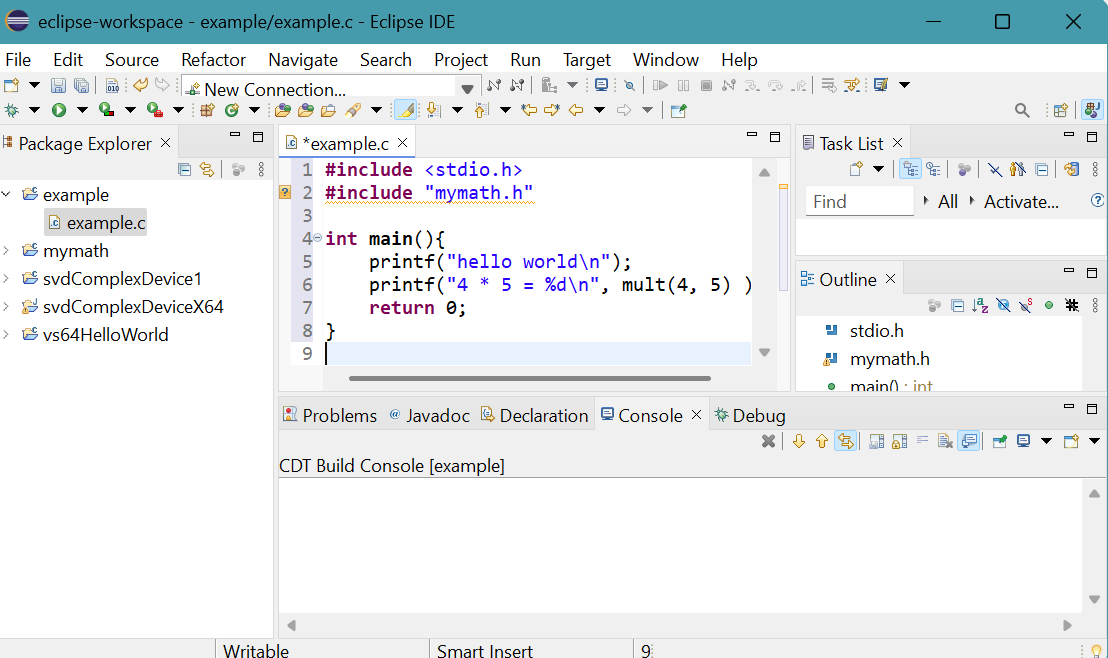
We must provide the pathway of mymath.h to compiler. It is in the folder of C shared library mymath project. - Right click the project name example in Package Explorer then select Properties.
Properties for example panel appears.
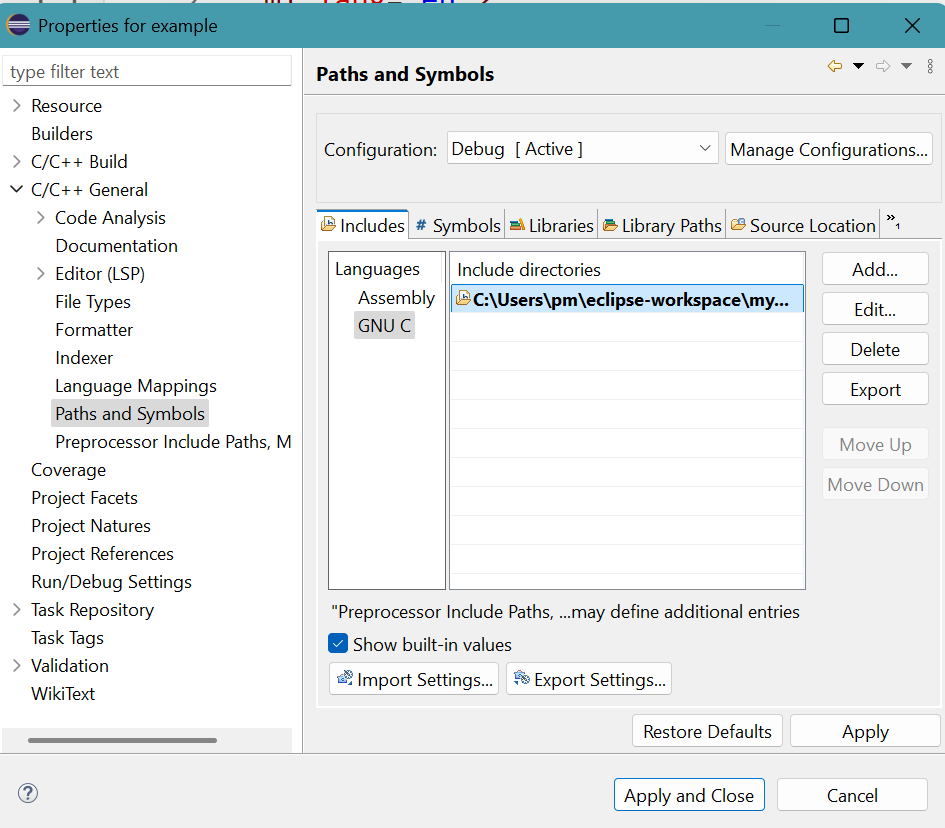
Click C/C++ General then Paths and Symbols.
Click GNU C in Includes tab.
Click Add... button.
Add directory path panel appears.
Provide the pathway:
C:\Users\pm\eclipse-workspace\mymathClick OK button.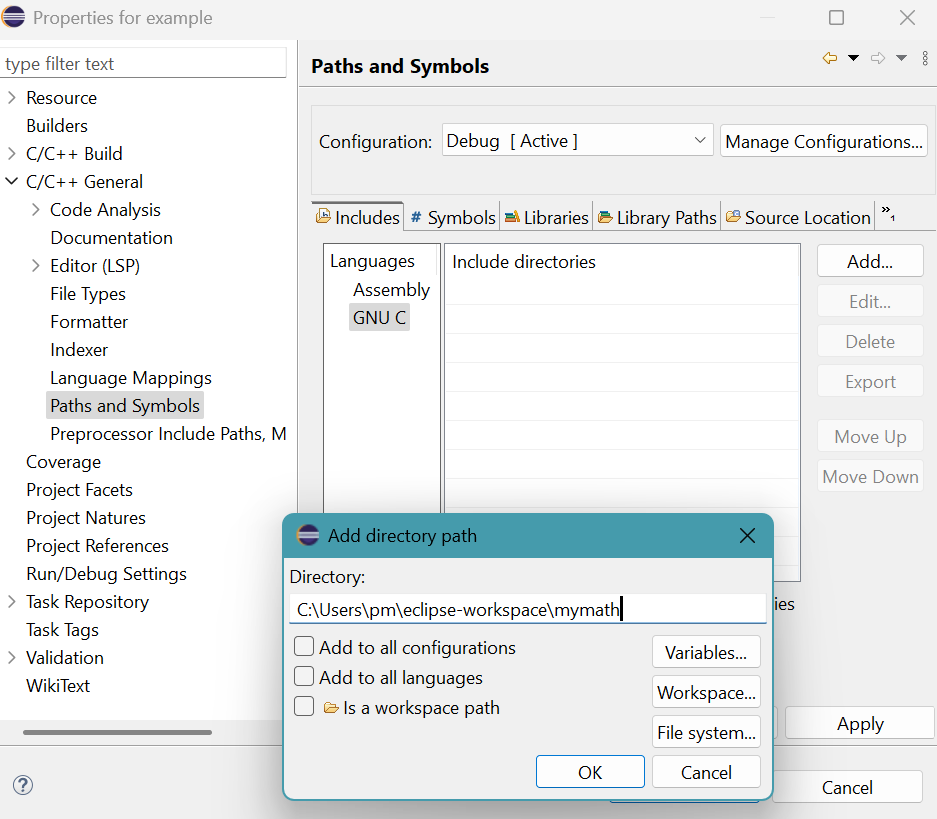
- The result is
Click Apply button.
- We must provide the filename mymath.dll required for this project
and its folder location
to linker. As a result, the later knows where the shared library is.
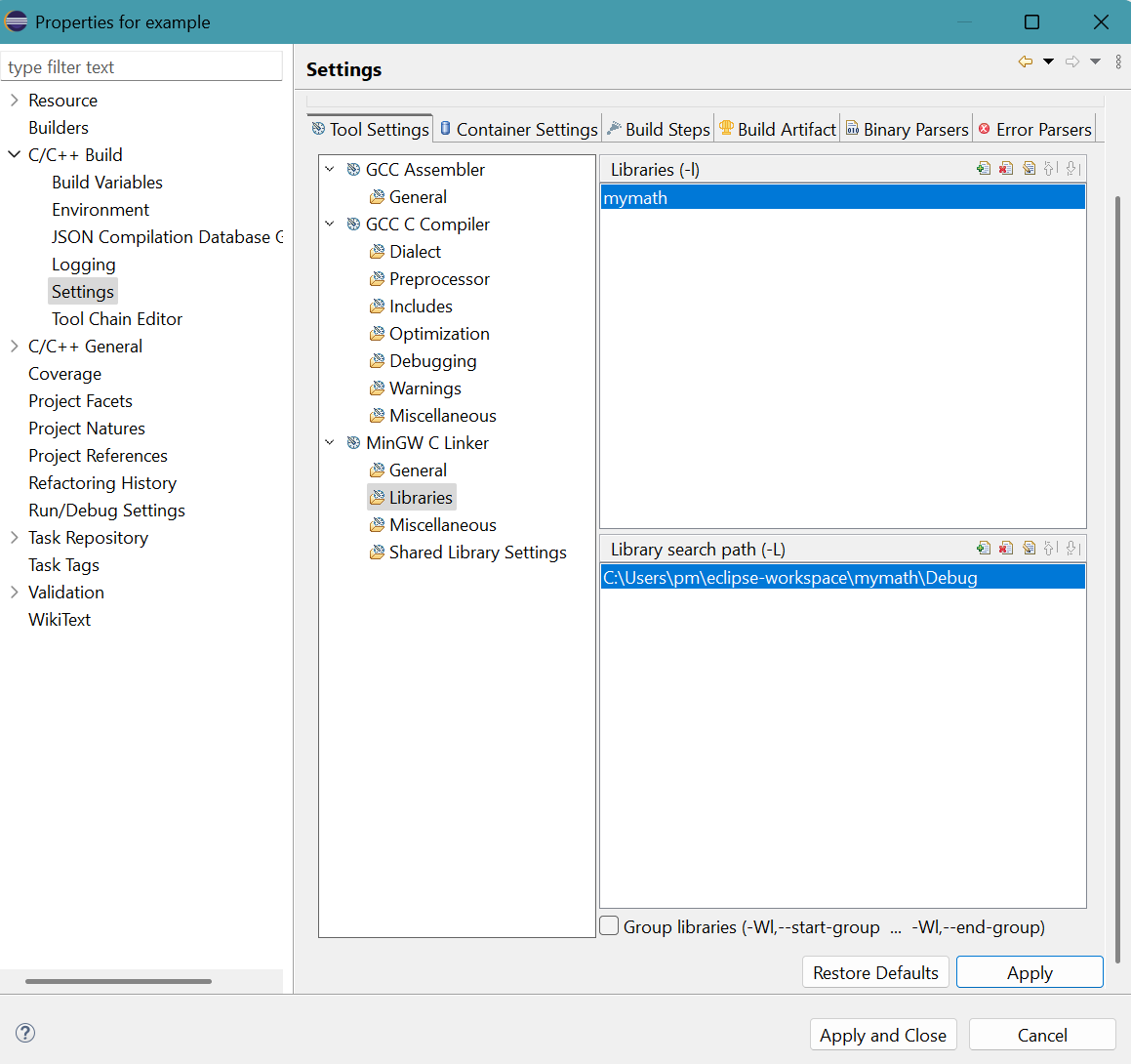
Click C/C++ Build then Settings.
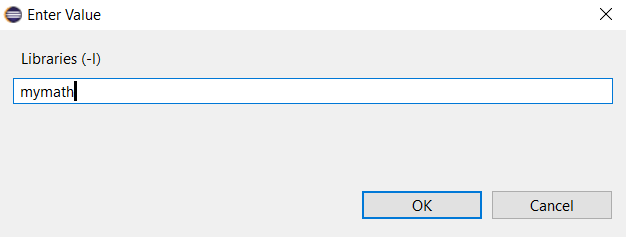
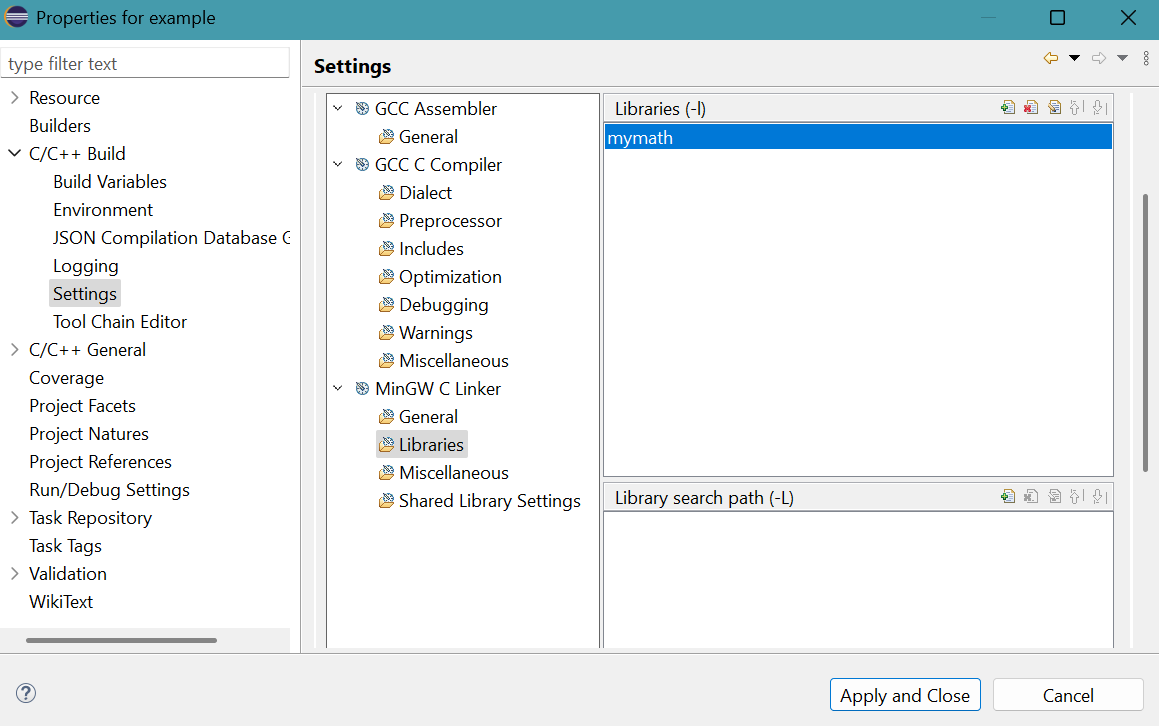
Click Libraries for MinGW C Linker in Tool Settings tab.Click + symbol in top part of Libraries (-l).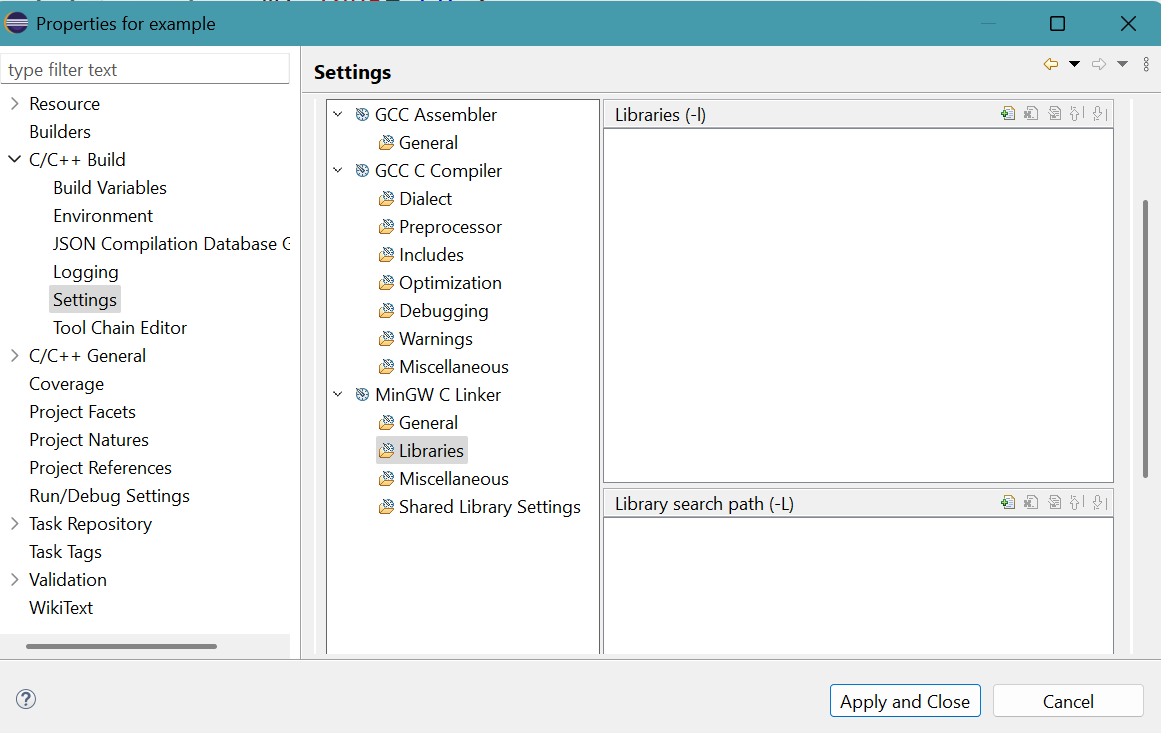
- Enter Value panel appears.
Provide mymath, the required DLL file without file extension.Click OK button. - The result is
Click + symbol in top part of Library search path (-L).
- Add directory path panel appears.
Provide the pathway of the project folder containing the required DLL file:
C:\Users\pm\eclipse-workspace\mymath\Debug
Click OK button.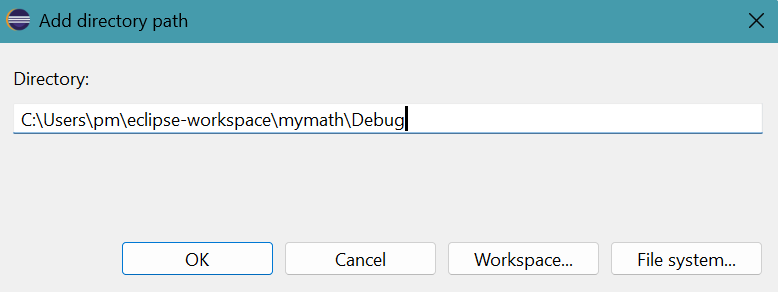
- The result is
Click Apply button.
- Change user environment variable so that the operating system Windows 11 knows
where the shared library mymath.dll is during the run time of example.exe.
Click Environment of C/C++ Build.
Select PATH.
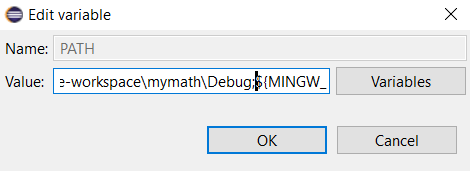
Click Edit... button.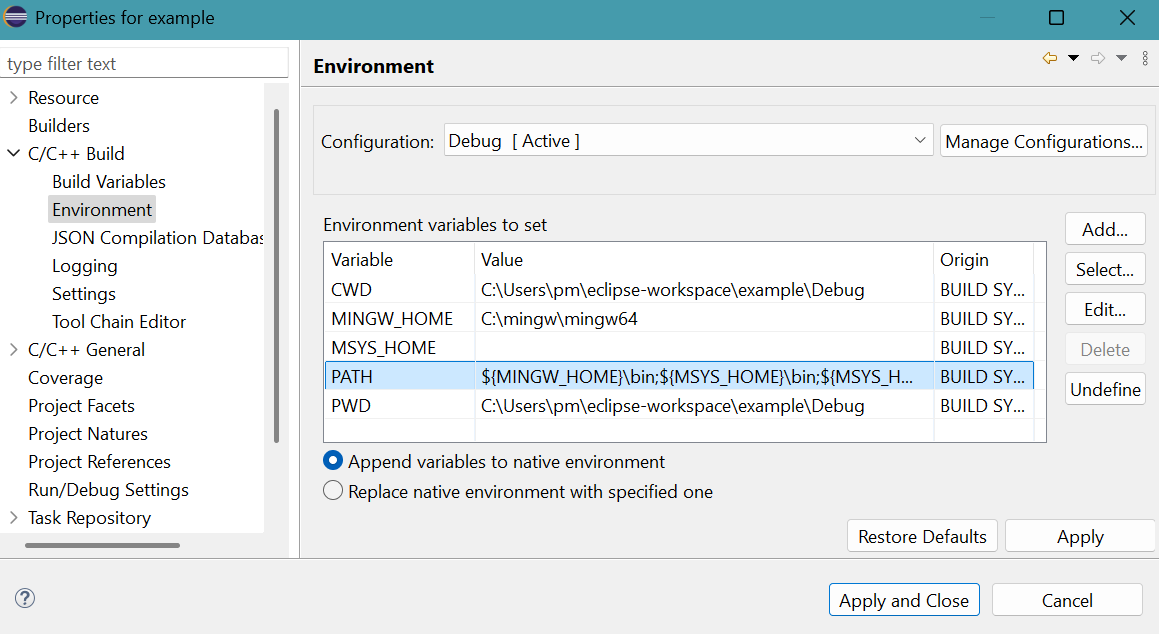
- Edit variable panel appears.
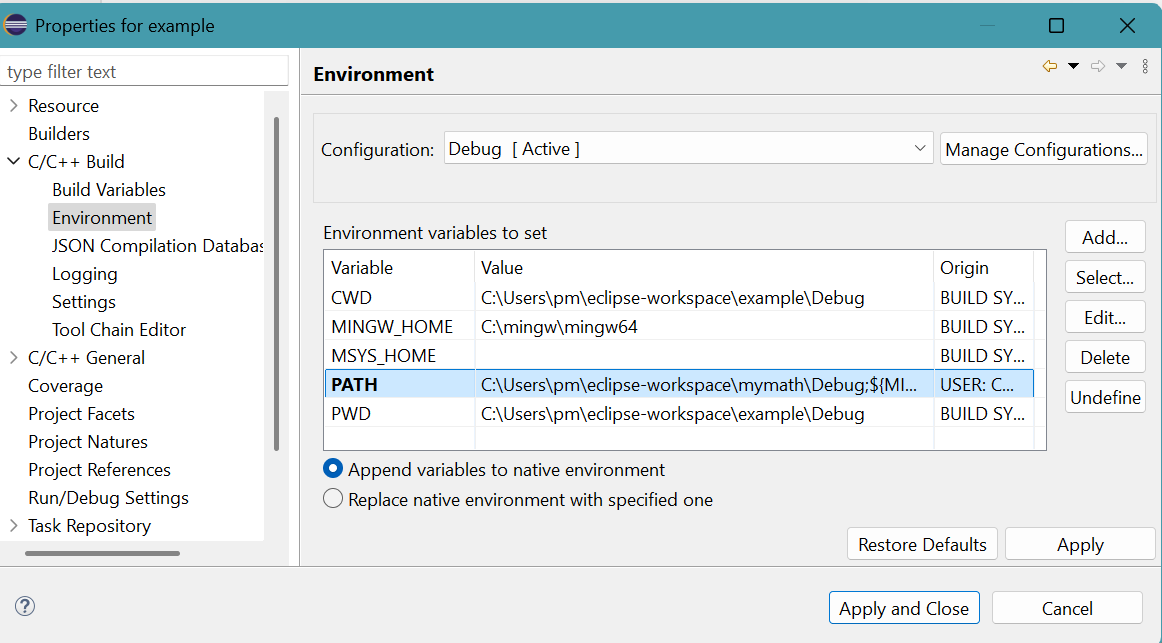
Insert the path: C:\Users\pm\eclipse-workspace\mymath\Debug;Click OK button. - The result is
Click Apply and Close button.
- The project before Build.
Press Ctrl S to save example.c.
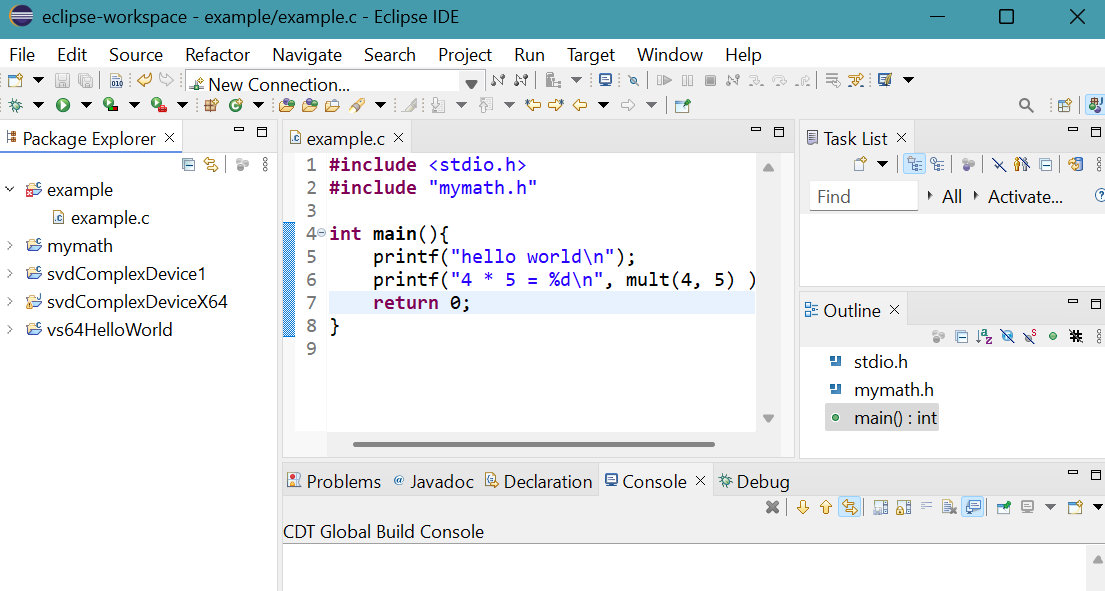
- Select Project menu then Build Projet.
64-bit example.exe file is generated in Debug folder.
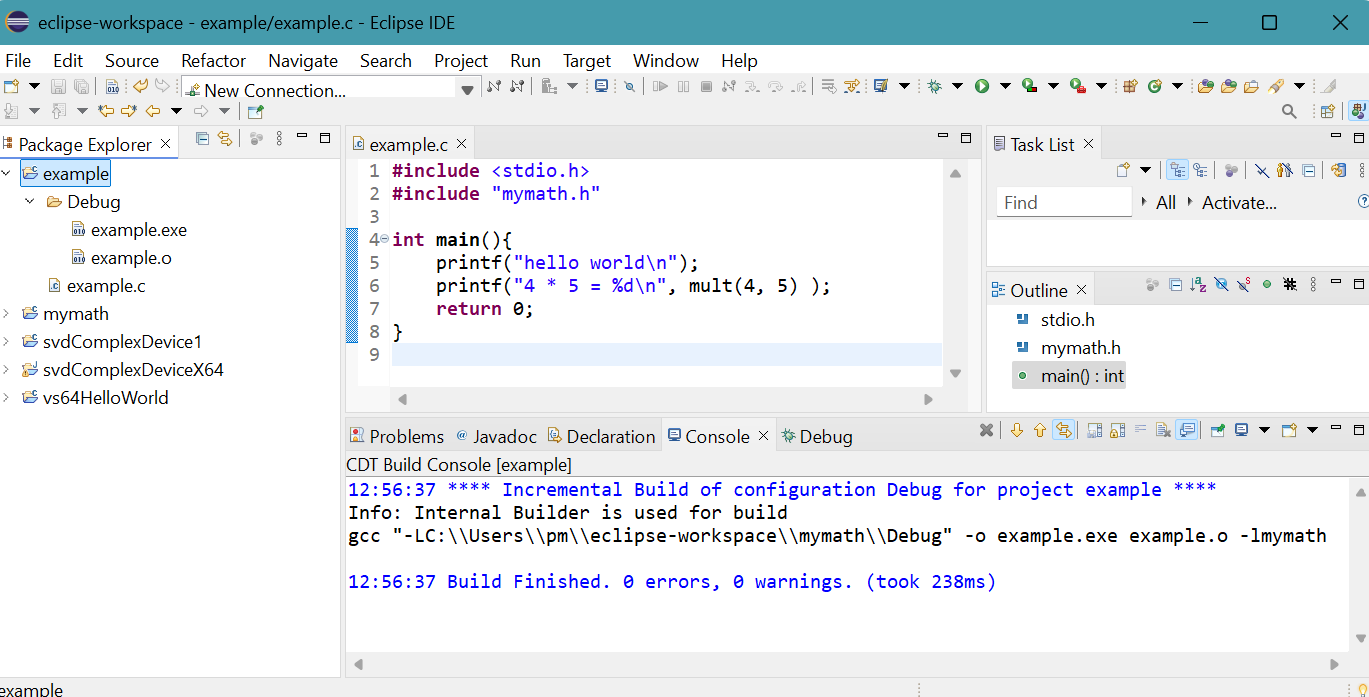
- Select Run menu then Run.
Select Local C/C++ Application then click OK button.
- Select Run menu then Run.
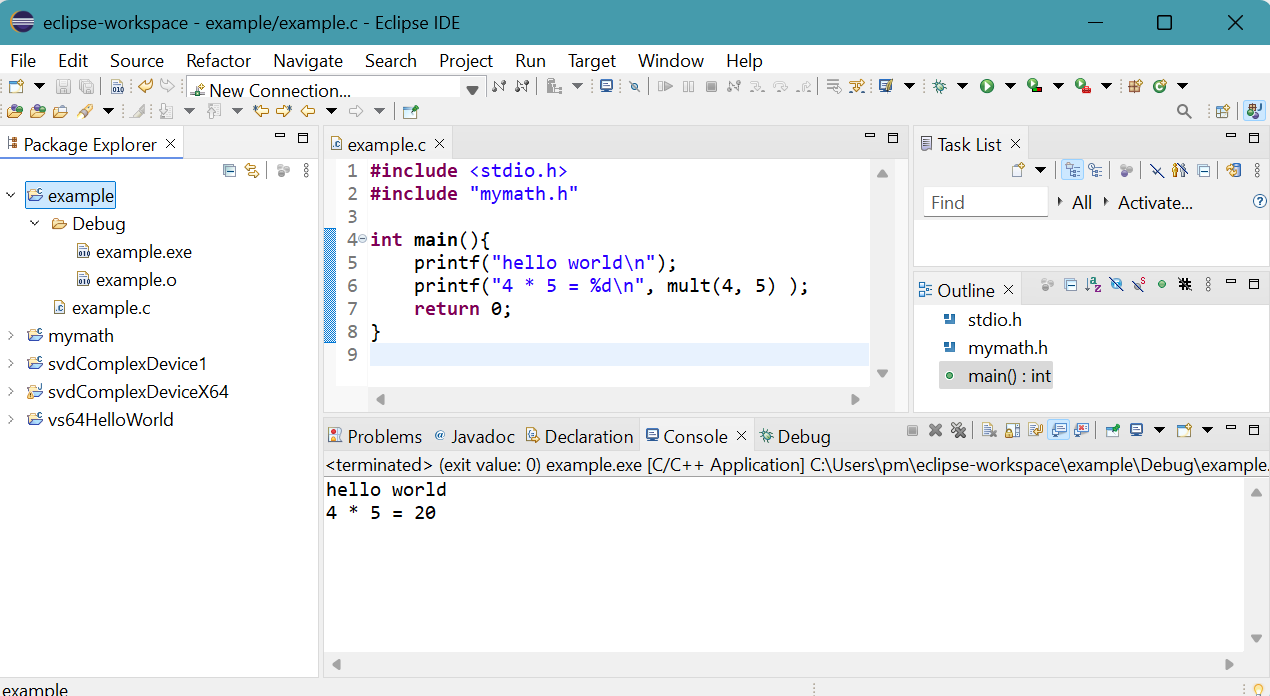
The result appears on Console panel.
C++ 64-bit shared library svdComplexDevice1.dll project with MinGW toolchain in Eclipse IDE
- Launch Eclipse IDE for Java Developers.
Press CTRL N.
Select a wizard panel appears.
Select C/C++ folder then C/C++ Project.
Click Next > button.
New C/C++ Project panel appears.
Select C++ Managed Build.
Click Next > button.
C++ Project panel appears.
Provide the project name: svdComplexDevice1
Select Empty Project for Shared Library.
Select MinGW GCC for Toolchains.Click Finish button.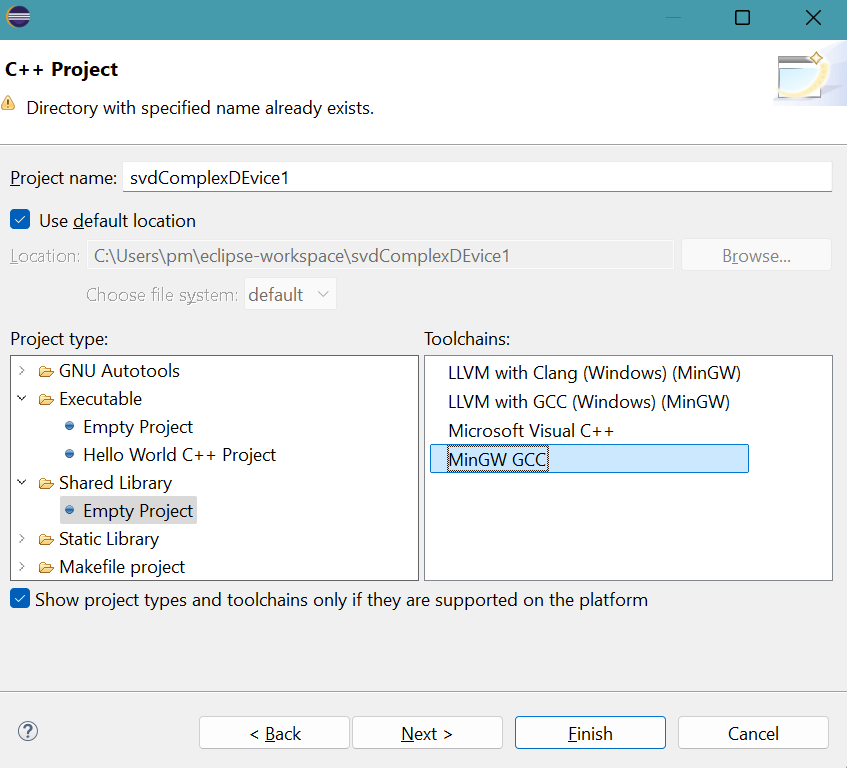
- The project folder svdComplexDevice1 appears in Package Explorer of Eclipse.
- Right click the project folder svdComplexDevice1.
Select New, then File.
Create New File panel appears.
Provide the File name: svdComplexDevice1.hClick Finish button.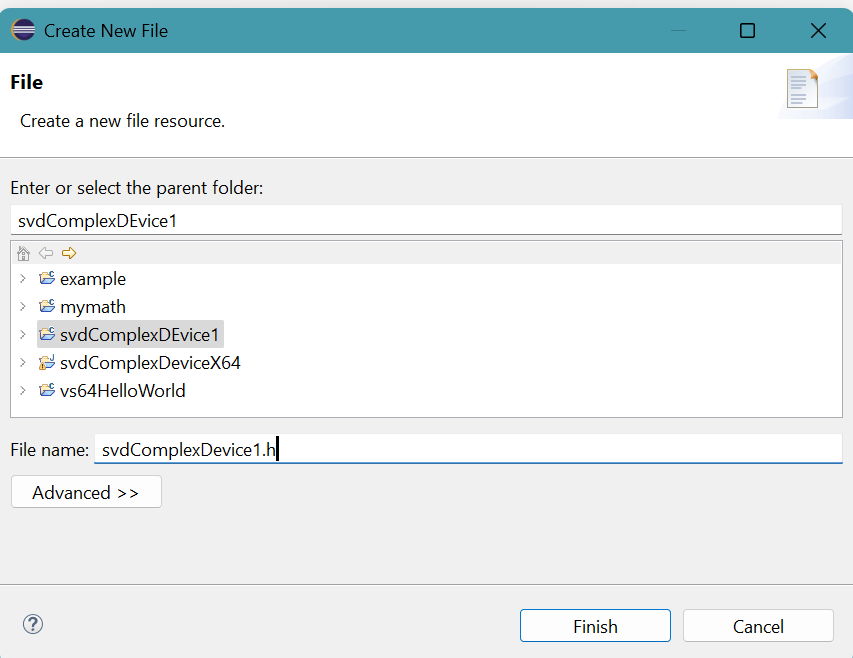
- Copy and past svdComplexDevice1.h
file into the newly created header file.
Press Ctrl S to save svdComplexDevice1.h.
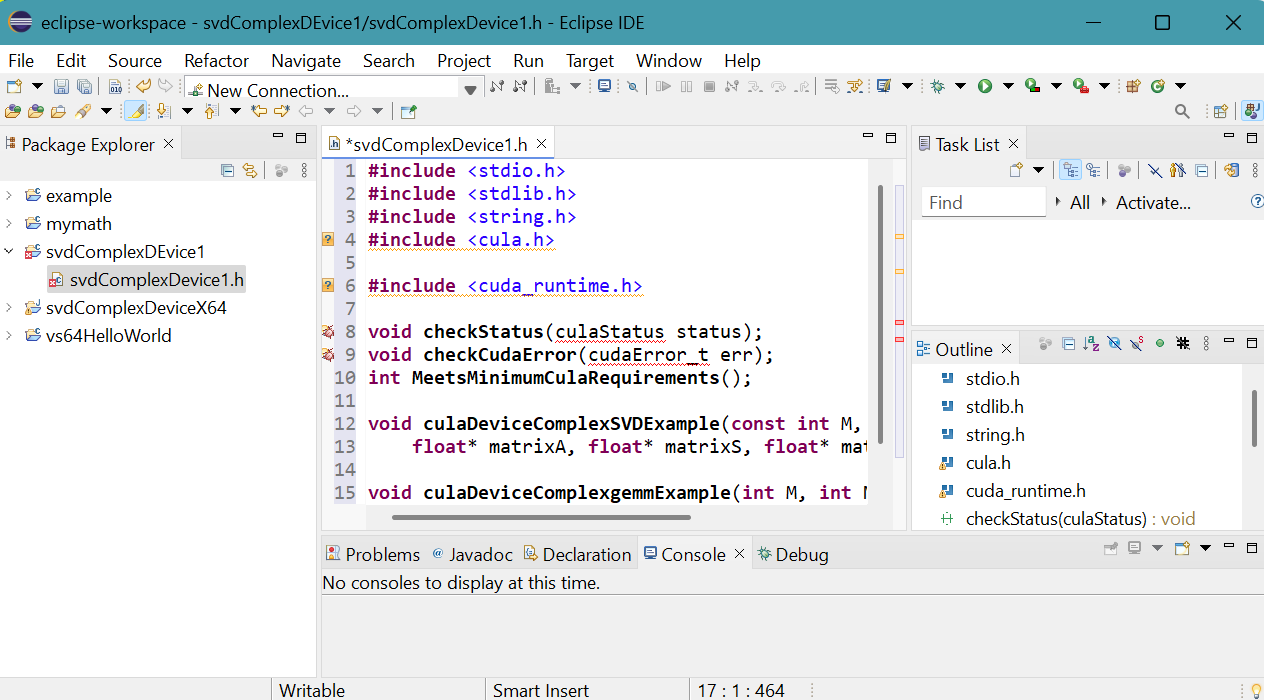
- Similarly, create the empty file svdComplexDevice1.cpp
- Copy and past svdComplexDevice1.cpp
file into the newly created file.
Press Ctrl S to save svdComplexDevice1.cpp.
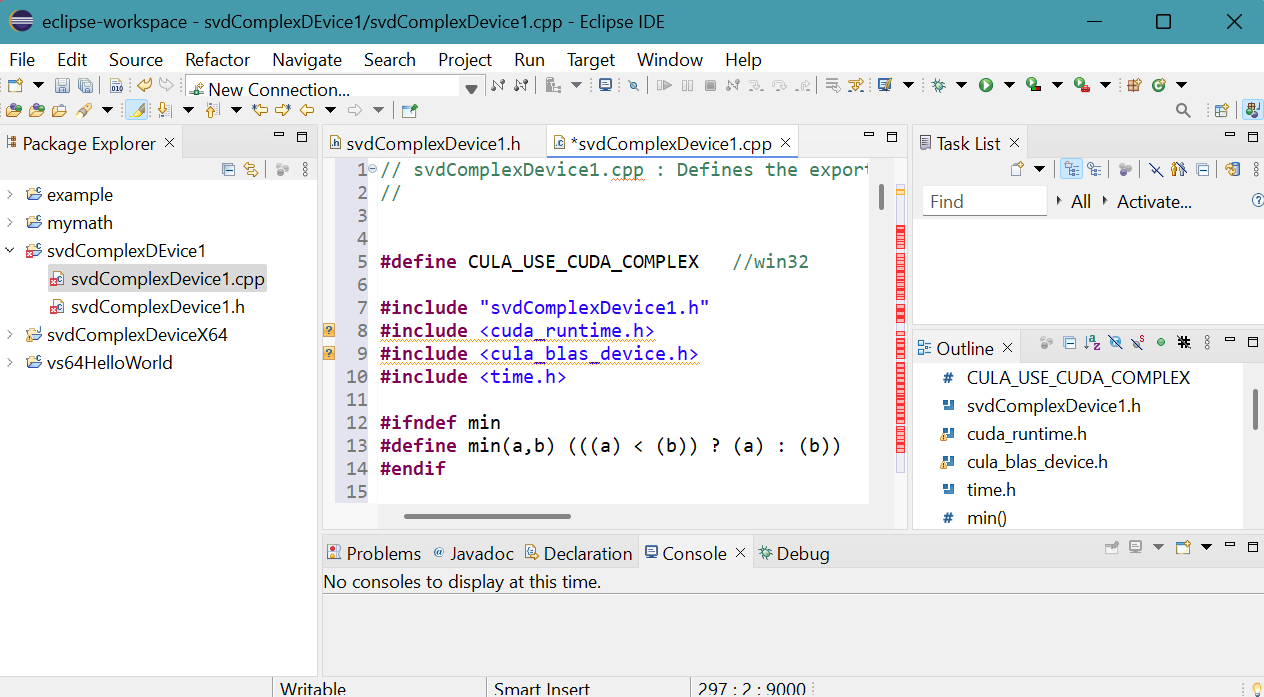
- Provide the path of include folder of CUDA and that of CULA to compiler.
Include folder contains header files.
Right click svdComplexDevice1 project in Package Explorer then select Properties.
Properties for svdComplexDevice1 panel appears.
Click Settings in C/C++ Build.
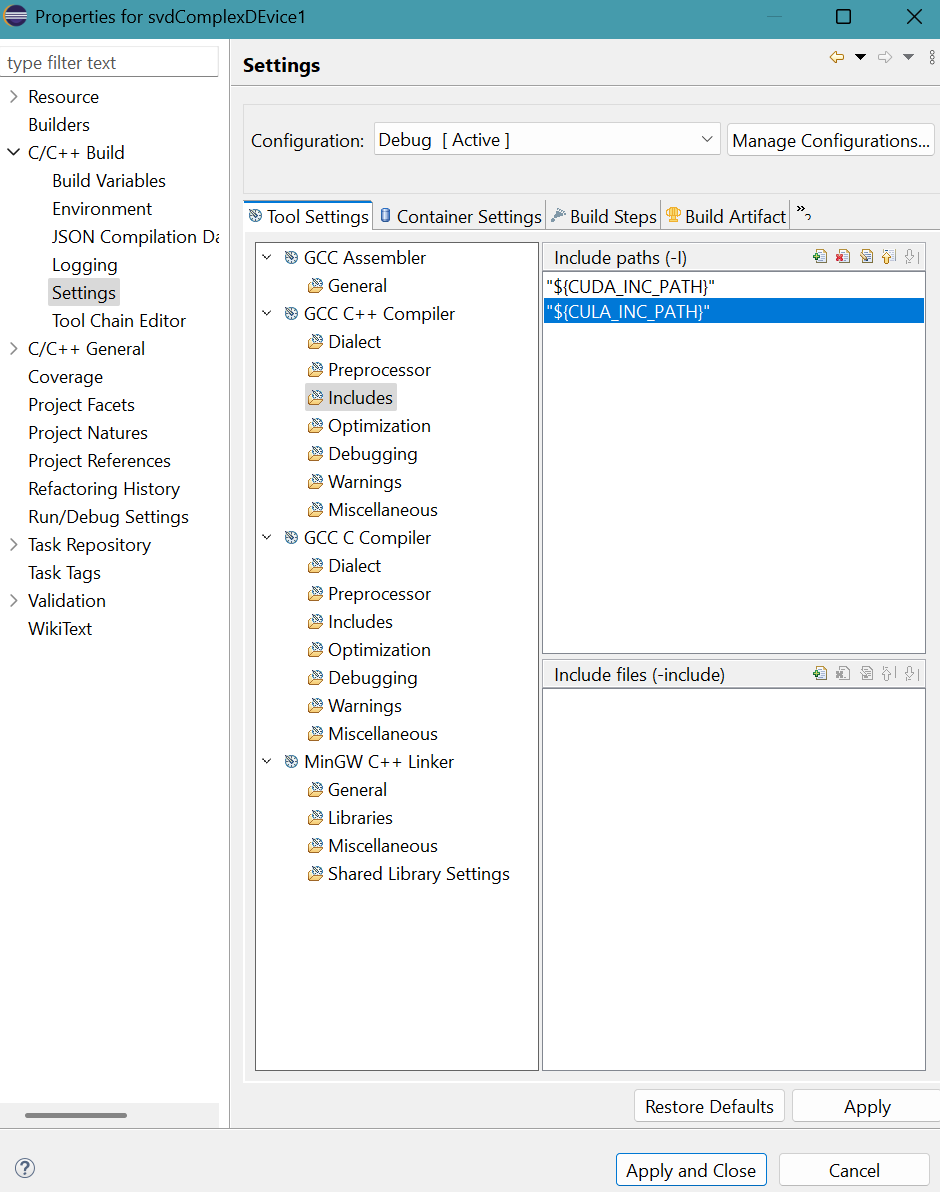
Click Includes for GCC C++ Compiler in Tool Settings tab.Click + symbol in top part of Include paths (-I).
- Add directoriy path panel appears.
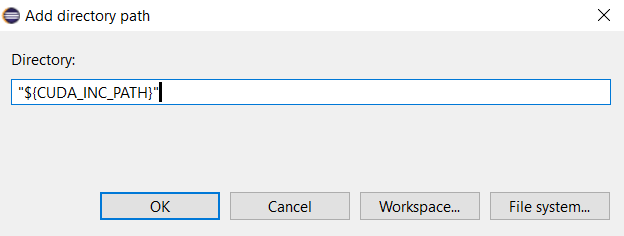
Provide "${CUDA_INC_PATH}" for Directory.
Directory must be enclosed in double quotes because this path contains space characters.Click OK button. - Similarly, provide the second path: "${CULA_INC_PATH}"
Click Apply button.
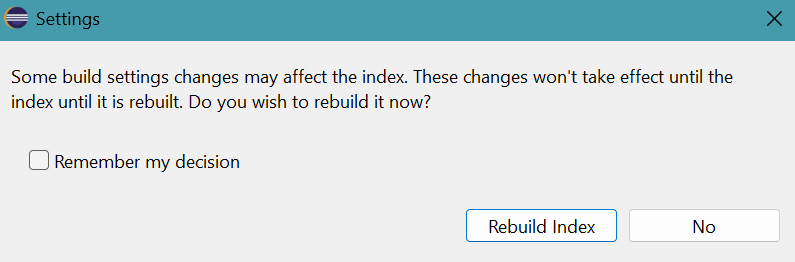
- A message apears.
Click Rebuild Index button.
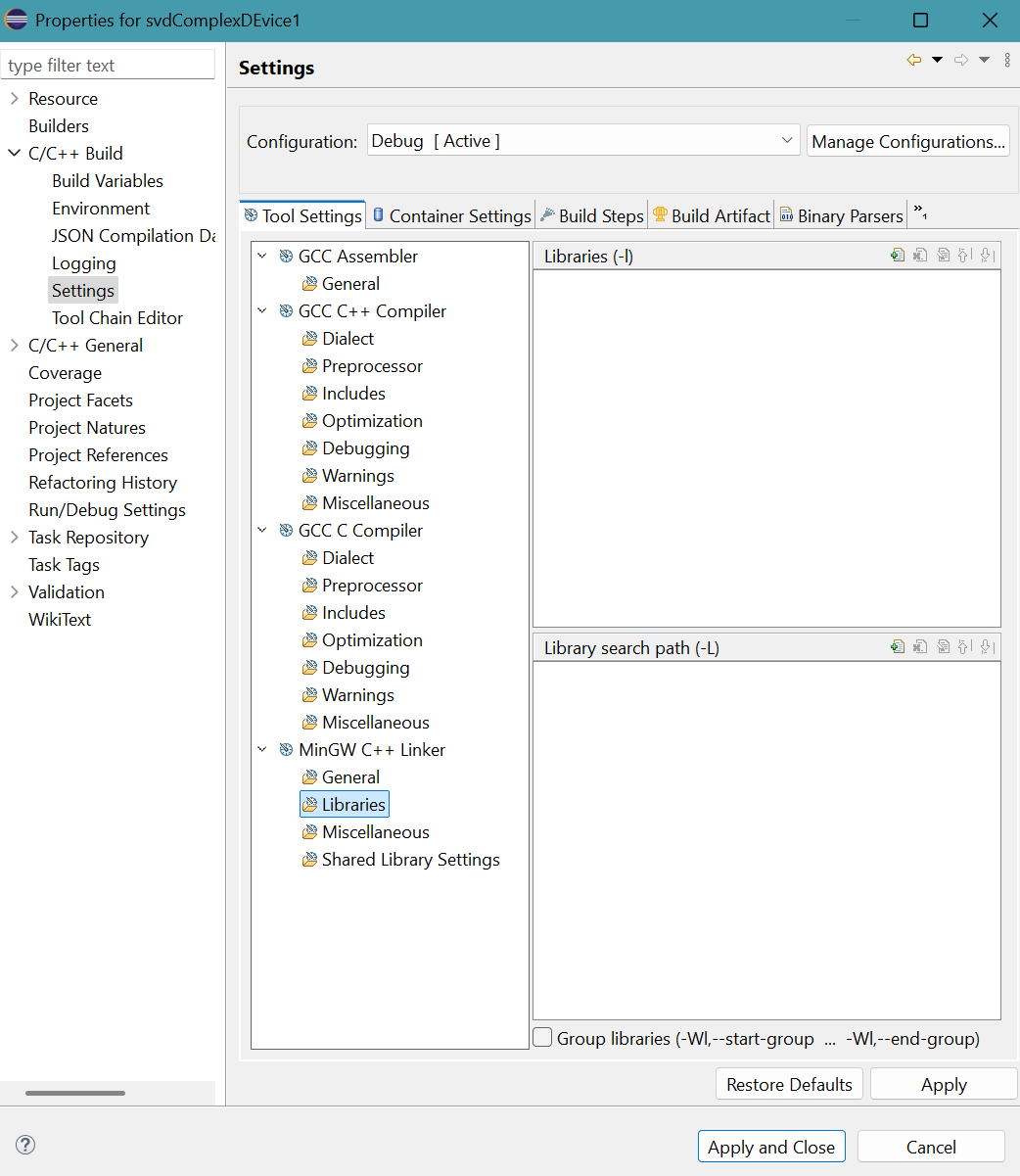
- Provide four libraries (cula_core.lib, cublas.lib,
cudart.lib, and cula_lapack.lib)
and their folder location ("${CUDA_LIB_PATH_64}" and
"${CULA_LIB_PATH_64}")
to the linker.
Click Libraries for MinGW C++ Linker in Tool Settings tab.
- The result is:
Library file names are provided without extension .lib and paths are enclosed in double quotes.
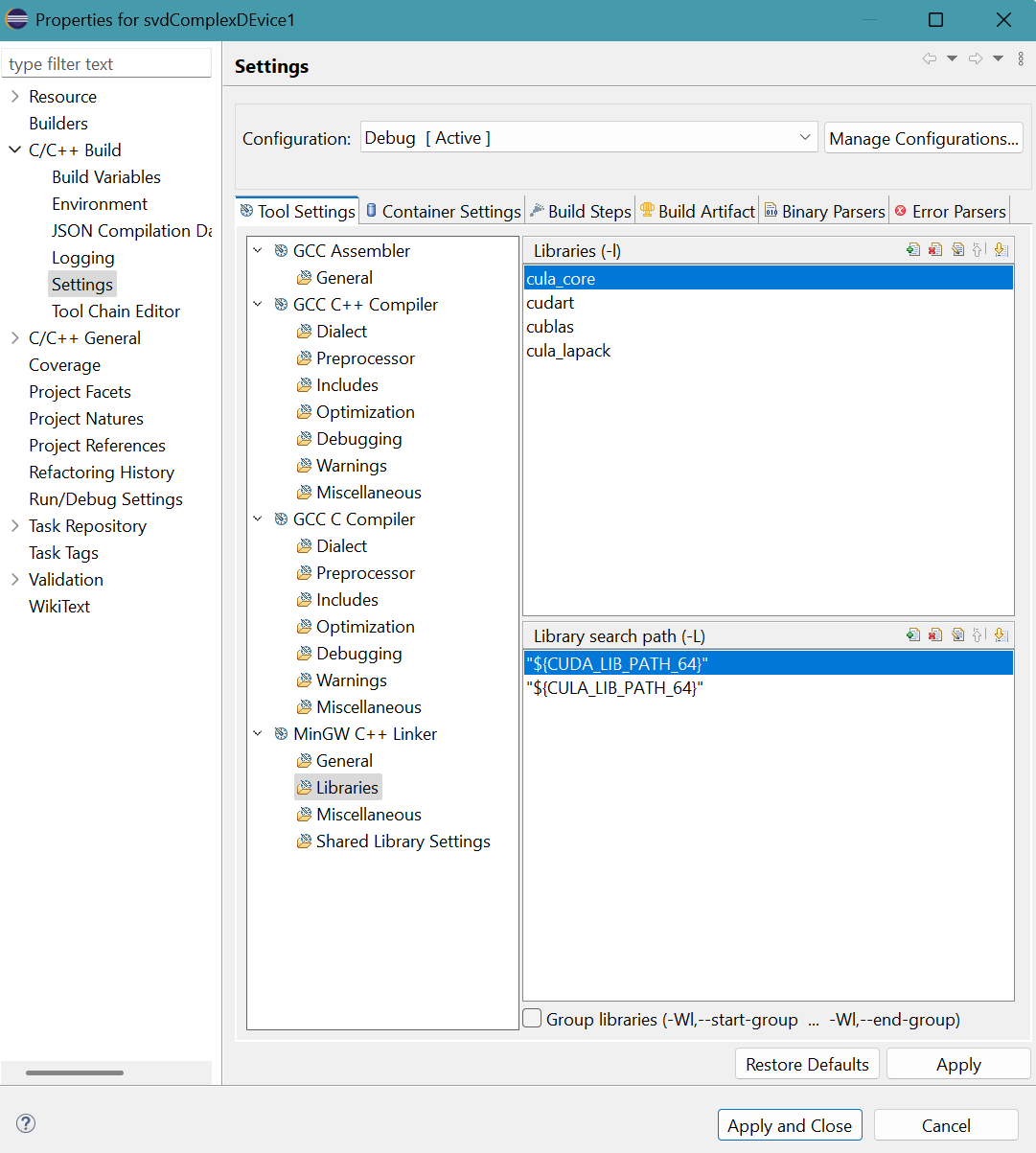
Click Apply button.
- Click Build Artifact tab.
Delete lib in Output prefix.
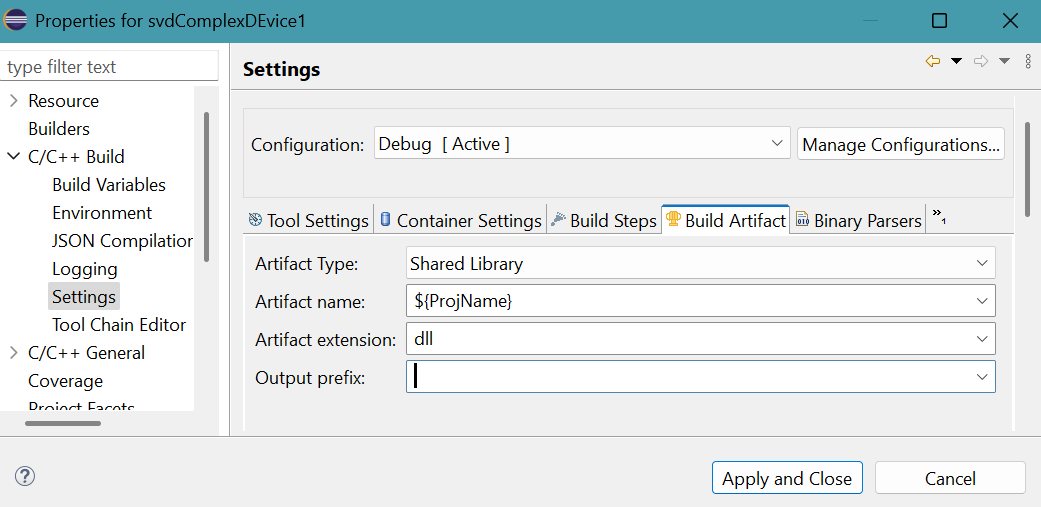
Click Apply and Close button.
- The project before Build.
- Select Project menu then Build Projet.
64-bit svdComplexDevice1.dll file with 246 kbit size is generated in Debug folder.
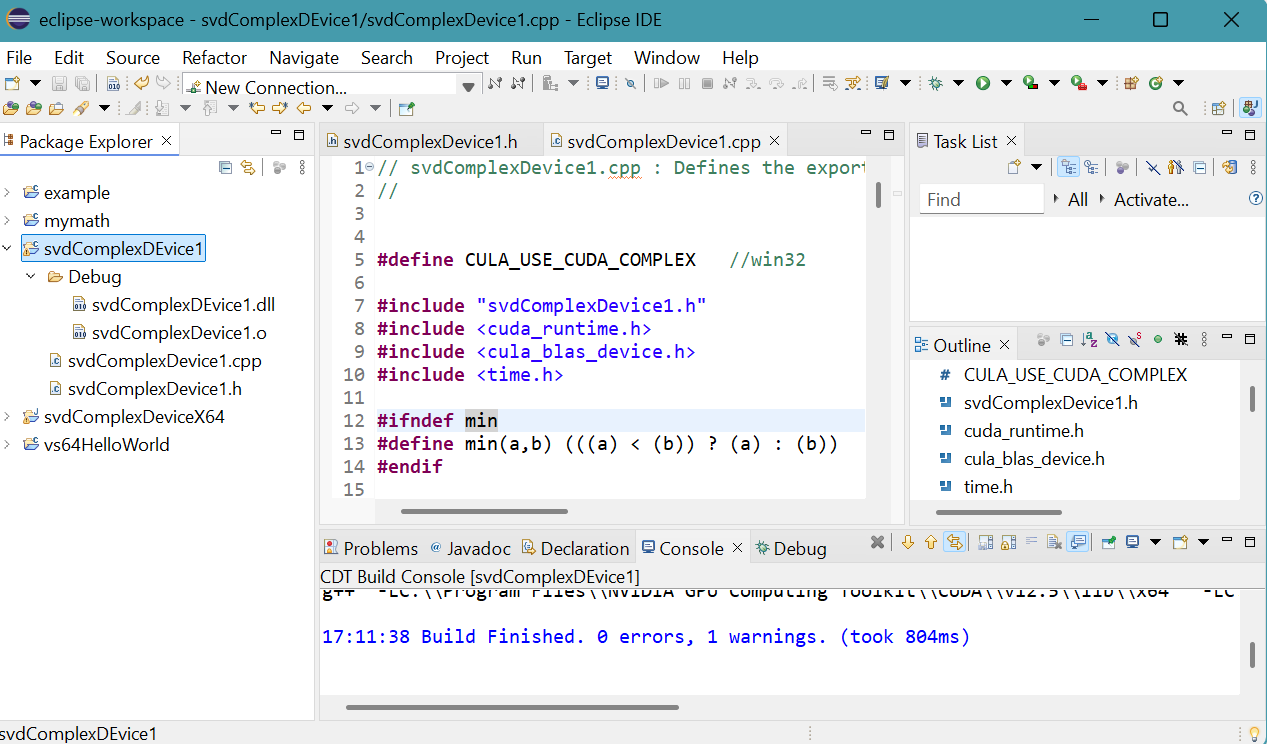
A message appears on CDT Build Console.
Various references
- Eclipse Foundation:
It is essential that the installation path does not contain any spaces. Therefore, you cannot install MinGW-w64 in Program Files. We recommend to create a folder mingw-w64 on your system drive (e.g., C:\mingw). - YouTube: How to install MinGW (GCC/G++) compiler in Windows 11 (2025)
- Transmissin Zero: Build Windows DLLs with MinGW
- Cygwin: Building and using DLLs
- cplusplus: How to create and use DLL's
- Stratman, Forex Factory: C++ dll tutorials using Eclipse
- Capsis: A complete Java - C++ connection example with mingw/g++ and JNA under Windows 64 bits
- Elias Volanakis, Eclipse Source:
Shared libraries with Eclipse CDT and cygwin on Windows
The compiler and linker will not find the header files / library unless you set the appropriate parameters. The compiler needs an include path (-I). The linker needs the library name (-l) and library search path (-L). These settings are scattered in two places in the project properties. Their location is not obvious for a first-time user. - Erich Styger, MCU on Eclipse: Eclipse build variables
- Erich Styger, MCU on Eclipse: Debug vs. release?
- OpenCV: Using OpenCV with Eclipse (plugin CDT)
- Syntax Scenarios: Install MinGW on Windows to run a C program
- Grenoble-inp: Compilation séparée et options de gcc
- Grenoble-inp: Programmation C et C++ - Utiliser le compilateur GCC