Example 1 of MQMAS simulation
The example deals with the central-transition echo amplitude of a spin I = 3/2 in a powder sample rotating at the magic angle with a rotor speed of 10 kHz.
The strength of the RF magnetic field is 100 kHz.
The values of the two quadrupole parameters are 1000 kHz for the quadrupole coupling constant QCC and 0 for the asymmetry parameter eta.
The simulated experiment associated with the MQMAS sequence is A(p1)B(), where the first-pulse length p1 increases from 0 to 20 µs by 0.5 µs step; the second-pulse length p2 is 1.5 µs.
The pulse length to pulse increment ratios are integers.
The number of integration steps for alpha and for beta Euler angles are MaxAlpha = 20, that for gamma Euler angle is MaxGamma = 10.
The first pulse excites the -3-quantum coherence only.
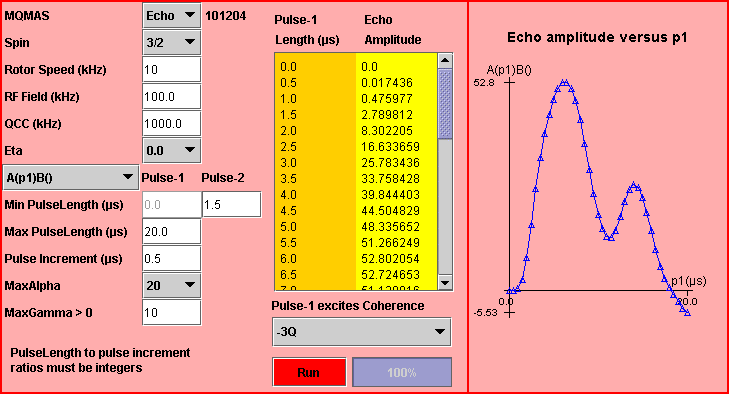
The sign of the central-transition echo amplitude does not change for a long range of the first-pulse length p1. This curve is identical to that obtained in Example 1 of two-pulse MAS simulation, but with higher amplitude.
