Wigner rotation matrices for second-rank spherical tensor
*** Outline ***
A. Wigner active rotation matrix
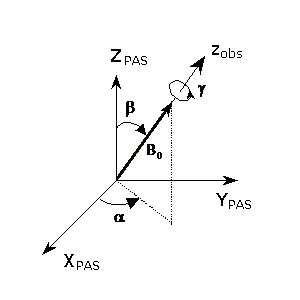
For static crystal, the orientation of the static magnetic field B0 in the principal-axis system (主軸坐標系) of the EFG tensor (XPAS, YPAS, ZPAS) is described with the Euler angles α, β, and γ (see EasySpin, Wikipedia, Wolfram MathWorld).
The component V(2,k) of the second-rank spherical tensor V in the obs coordinate frame is:
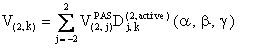 Equation 1
Equation 1
The Wigner matrix for active rotation is:
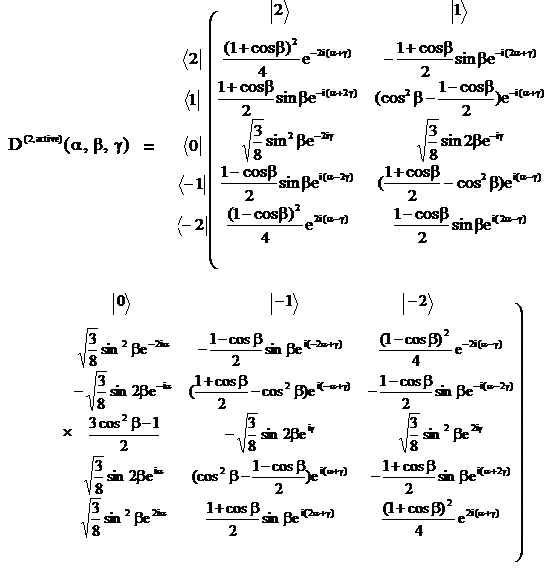
Reference
-
J. Pagaran, S. Fritzsche, and G. Gaigalas
Maple procedures for the coupling of angular momenta. IX. Wigner D-functions and rotation matrices,
Comput. Phys. Commun. 174, 616-630 (2006).
Abstract -
Melinda J. Duer
Introduction to Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy,
Blackwell, Oxford (2004).
Google book -
Kurt Gottfried and Tung-mow Yan
 Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals, Second edition
Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals, Second edition
Springer, New York (2003).
Google book, Pages 304-305 and 312-313.
-
Mattias Edén
Computer simulations in solid-state NMR. I. Spin dynamics theory,
Concepts Magn. Reson. 17A, 117-154 (2003).
Abstract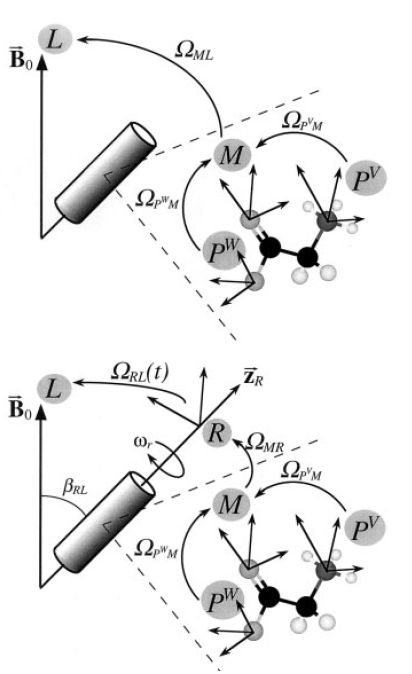 The transformation of the coordinate system F into the system F' is parametrized by the triplet of Euler angles {αFF', βFF', γFF'}. The subscripts FF' specify a transformation from system F to system F'.
The transformation of the coordinate system F into the system F' is parametrized by the triplet of Euler angles {αFF', βFF', γFF'}. The subscripts FF' specify a transformation from system F to system F'. -
Bernhard Blümich
NMR Imaging of Materials,
Clarenton, Oxford (2000).
Google book, Pages 77-78. -
P. Hodgkinson and L. Emsley
Numerical simulation of solid-state NMR experiment,
Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 36, 201-239 (2000).
Abstract -
Albert Messiah
Quantum Mechanics, two volumes bound as one
Dover, Mineola (1999).
Google book, Pages 523-538 and 1068-1075. -
O. N. Antzutkin
Sideband manipulation in magic-angle-spinning nuclear magnetic resonance,
Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 35, 203-266 (1999).
Abstract
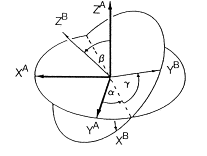 Euler angles in the rotational transformation from a frame A to a frame B. The unitary transformation of a spherical tensor can be expressed as
Euler angles in the rotational transformation from a frame A to a frame B. The unitary transformation of a spherical tensor can be expressed as
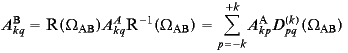
-
Masud Chaichian and Rolf Hagedorn
 Symmetries in Quantum Mechanics: From Angular Momentum to Supersymmetry,
Symmetries in Quantum Mechanics: From Angular Momentum to Supersymmetry,
Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol (1998), Page 183.
-
Leslie E. Ballentine
 Quantum Mechanics: A Modern Development,
Quantum Mechanics: A Modern Development,
World Scientific, Singapore (1998).
Google book, Pages 176-182.
-
Anthony J. Stone
The Theory of Intermolecular Forces,
Oxford University Press, New York (1996).
Google book, Appendix B. -
P. P. Man
Quadrupolar interactions (PDF article, 2.3 Mb),
in Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
D. M. Grant and R. K. Harris Eds.
J. Wiley, Chichester, Pages 3838-3848 (1996). -
Fl. Stancu
 Group Theory in Subnuclear Physics,
Group Theory in Subnuclear Physics,
Oxford University Press, New York (1996).
Google book, Pages 209-219, Erratum -
Ronald Y. Dong
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Liquid Crystals,
Springer-Verlag, New York (1994). -
Klaus Schmidt-Rohr and Hans Wolfgang Spiess
Multidimensional Solid-State NMR and Polymers,
Academic, London (1994), Pages 444-452. -
V. K. Thankappan
 Quantum Mechanics, Second edition
Quantum Mechanics, Second edition
New Age International, New Dehli (1993).
Google book -
D. A. Varshalovich, A. N. Moskalev, and V. K. Khersonskii
Quantum Theory of Angular Momentum, Irreducible Tensors, Spherical Harmonics, Vector Coupling Coefficients, 3nj Symbols
World Scientific, Singapore (1988). -
M. A. Morrison and G. A. Parker
A guide to rotations in quantum mechanics,
Aust. J. Phys. 40, 465-497 (1987).
PDF file, PDF file -
George Arfken
 Mathematical Methods for Physicists, Third edition
Mathematical Methods for Physicists, Third edition
Academic, Boston (1985), Pages 258-261. -
M. Mehring
Principles of High Resolution NMR in Solids, Second, revised and enlarged edition
Springel-Verlag, Berlin (1983), Pages 19-23. -
Hans Wolfgang Spiess
Rotation of Molecules and Nuclear Spin Relaxation,
in NMR Basic Principles and Progress, Vol. 15
P. Diehl, E. Fluck, and R. Kosfeld Eds.
Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1978), Pages 202-204.
The Eulerian angles β and α simply are the polar angles of the z axis in the principal axes system X, Y, Z.
-
D. M. Brink and G. R. Satchler
Angular Momentum, Second edition
Clarendon Press, Oxford (1968).
PDF file
B. Wigner passive rotation matrix
For static crystal, the orientation of the principal-axis system (主軸坐標系) of the EFG tensor (XPAS, YPAS, ZPAS) in the static magnetic field B0 (xobs, yobs, zobs) is described with the Euler angles α, β, and γ.
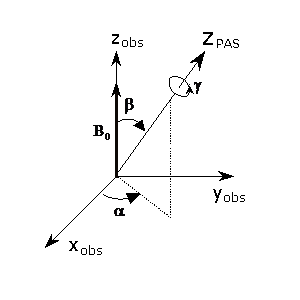
The component V(2,k) of the second-rank spherical tensor V in the obs coordinate frame is:
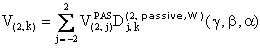 Equation 2
Equation 2The Wigner matrix for passive rotation is:
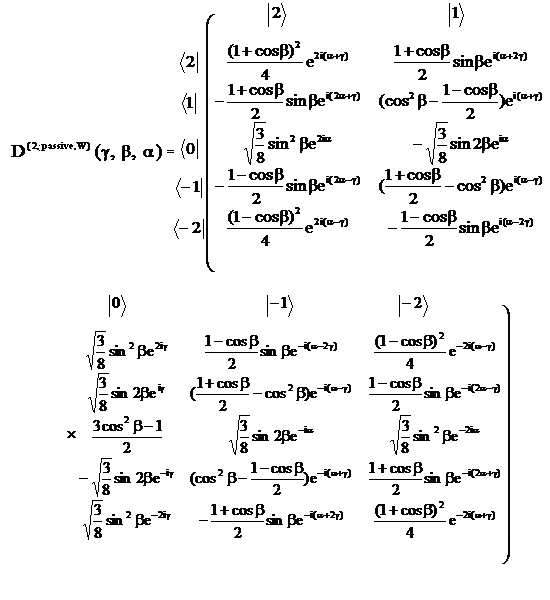
Reference
-
J. Van de Wiele
Rotations et moments angulaires en mécanique quantique,
Ann. Phys. Fr. 26, 1-169 (2001).
PDF file, Abstract -
D. Freude
Quadrupolar nuclei in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (PDF article),
in Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry
R. A. Meyers Ed.
J. Wiley, Chichester, Pages 12188-12224 (2000). -
B. F. Chmelka and J. W. Zwanziger
Solid-state NMR line narrowing methods for quadrupolar nuclei: Double rotation and dynamic-angle spinning,
in NMR Basic Principles and Progress, Vol. 33, Pages 79-124
P. Diehl, E. Fluck, H. Günther, R. Kosfeld, and J. Seelig Eds.
B. Blümich (Guest Editor)
Springer, Berlin (1994). -
D. Freude and J. Haase
Quadrupole effects in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance,
in NMR Basic Principles and Progress, Vol. 29, Pages 1-90
P. Diehl, E. Fluck, H. Günther, R. Kosfeld, and J. Seelig Eds.
Springer, Berlin (1993). -
G. Engelhardt and D. Michel
High-Resolution Solid-State NMR of Silicates and Zeolites,
Wiley, Chichester (1987). -
Karl Blum
 Density Matrix - Theory and Applications,
Density Matrix - Theory and Applications,
Plenum, New York (1981).
Google book, Pages 89-91 and 208 -
Mitchel Weissbluth
Atoms and Molecules, Student edition
Academic, New York (1978).
The Wigner passive rotation matrix presented in this book is D(2, passive,W)(α, β, γ).
-
Ulrich Haeberlen
High Resolution NMR in Solids, Selective Averaging,
Academic, New York (1976), Pages 11-12.
The three angles α, β, and γ are the Euler angles by which the laboratory frame can be brought into coincidence with the principal axis system.
-
A. R. Edmonds
Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics, third printing with corrections
Princeton University Press, Princeton (1977).
In the following discussions the term rotation will be interpretated as a rotation of the frame of reference about the origin, the field points (i.e. the physical system) being supposed fixe. Each point of the 3-dimensional space is thus given new coordinates, which are functions of the old coordinates and of the parameters which describe the rotation, namely the Euler angles.
-
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifchitz
Quantum Mechanics, Non-Relativistic Theory, 3rd edition, revised and enlarged,
translated from the Russian by J. B. Sykes and J. S. Bell,
in Course of Theoretical Physics, Volume 3
Pergamon, Oxford (1976), Pages 216-218. -
Brian L. Silver
Irreducible Tensor Methods, AN INTRODUCTION FOR CHEMISTS,
Academic Pres, New York (1977)
PDF file -
L. Landau et E. Lifchitz
Mécanique Quantique, 3e Edition, remaniée et complétée avec la participation de L. Pitayevski,
traduit du russe par Edouard Gloukhian,
dans la collection Physique Théorique, Tome 3
MIR, Moscou (1975), Pages 250-255. -
V. B. Berestetskii, E. M. Lifshitz, and L. P. Pitaevskii
Relativistic Quantum Theory, Volume 4 of Course of Theoretical Physics, Part 1
Pergamon Press, Oxford (1971), Pages 367-371. -
M. Bouten
On the rotation operators in quantum mechanics,
Physica 42, 572-580 (1969).
Abstract -
A. A. Wolf
Rotation operators,
Am. J. Phys. 37, 531-536 (1969).
Abstract
C. Conclusion
Both Equations 1 and 2 represent a passive rotation of the EFG tensor:
- from the PAS coordinate frame to the obs coordinate frame for Equation 1,
- from the obs coordinate frame to the PAS coordinate frame for Equation 2.
The Euler angles α, β, and γ in Equation 1 correspond to the Euler angles γ, β, and α in Equation 2, respectively.
Sometimes, Equation 2 is written in the following way:
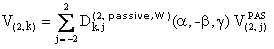 Equation 3
Equation 3The matrix D(2,passive,W)(α, -β, γ) in Equation 3 is the transpose of D(2,passive,W)(γ, β, α) defined in Equation 2.
Reference
-
Rytis Juršėnas and Gintaras Merkelis
The transformation of irreducible tensor operators under spherical functions,
Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 2230-2245 (2010).
Abstract -
Jeffrey W. Peng and Gerhard Wagner
Protein mobility from multiple 15N relaxation parameters,
in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Probes of Molecular Dynamics, Pages 373-454
Robert Tycko Ed.
Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (1994).
Google book -
Eugene P. Wigner
 Group Theory and Its Application to Quantum Mechanics of Atomic Spectra,
Volume 5 in Pure and Applied Physics,
Group Theory and Its Application to Quantum Mechanics of Atomic Spectra,
Volume 5 in Pure and Applied Physics,
translated from the Germain by J. J. Griffin
Academic Press, New York (1959), Pages 168-169, 357-359, and 362.
5 Mb DjVu file, DjVu viewer from DjVu.org
