
C14_4^51d: 1D double quantum / single quantum correlation C1445 pulse program for TopSpin2.1
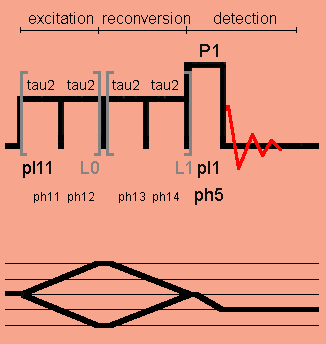
Since non-phase cycling is applied to the C14_4^5 excitation pulse, four-phase cycling is applied to the detection pulse P1 for selecting the 0Q -> -1Q coherence order jump, and four-phase cycling is applied to the C14_4^5 reconversion pulse for filtering DQ coherences.
;c14-4-51d (TopSpin 2.0) ;C14_4^5 1D sequence to set up C14_4^5 power level pl11 ;Avance II+ version ;parameters: ;d1 : recycle delay ;d20 : delay between saturation pulses ;p1 : f1 presaturation pulses and detection pulse at pl1 ;pl1 : Power level for detection pulse ;pl11 : Power level for C14_4^5 recoupling sequence B1=3.5*cnst31 in Hz ;cnst31 : spinning frequency ;l0 : number of excitation composite C14_4^5 cycles (usually a multiple of 14) ;l1 : number of reconversion composite C14_4^5 cycles (usually a multiple of 14) ;l20 : # of pulses in saturation pulse train ;ns : = 16*n ;zgoptns :-Dpresat or blank ;$COMMENT=DQ excitation C14_4^5 sequence ;$CLASS=Solids ;$DIM=1D ;$TYPE=direct excitation ;$SUBTYPE=homonuclear correlation ;$OWNER=Bruker define pulse tau2 "tau2=((1s/cnst31)/7)" ;180° pulse "d31=1s/cnst31" ;one rotor period ;cnst11 : to adjust t=0 for acquisition, if digmod = baseopt "acqt0=1u*cnst11" #include <rot_prot.incl> ;protect for too slow rotation ze ;acquire into a cleared memory 1 d31 #ifdef presat ;set with -Dpresat pres, d20 ;delay between saturation pulses (p1 pl1 ph1):f1 ;saturation loop lo to pres times l20 #endif /* presat */ 2 d1 ;recycle delay 1m rpp11 ;reset the phase ph11 pointer to the first element 1m rpp12 ;reset the phase ph12 pointer to the first element 1m rpp13 ;reset the phase ph13 pointer to the first element 1m rpp14 ;reset the phase ph14 pointer to the first element 1u pl11:f1 ;switch to C14_4^5 RF condition ;C14_4^5 excitation 3 (tau2 ph11 ipp11 ipp13 ipp14):f1 ;first 180° C14_4^5 excitation pulse at pl11 ;increment phase ph11 pointer ;increment reconversion pulse phase ph13 and ph14 pointers (tau2 ph12 ipp12):f1 ;second 180° C14_4^5 excitation pulse, ;increment phase ph12 pointer lo to 3 times l0 ;l0 = multiple of 14 ;C14_4^5 reconversion 4 (tau2 ph13 ipp13):f1 ;first 180° C14_4^5 reconversion pulse, ;increment phase ph13 pointer (tau2 ph14 ipp14):f1 ;second 180° C14_4^5 reconversion pulse, ;increment phase ph14 pointer lo to 4 times l1 ;l1 = multiple of 14 (p1 pl1 ph5):f1 ;detection pulse flips magnetization into the xy plane 2u gosc ph31 ;gosc does not loop to 1 ;start ADC with ph31 signal routing ;DQ filtering (four phase cycling): 1m ip13*16384 ;increments all phases of ph13 by 90° 1m ip14*16384 ;increments all phases of ph14 by 90° lo to 1 times ns ;next scan 100m wr #0 ;save data on disk HaltAcqu, 1m exit ph1= 0 ;for saturation pulses ph11=(65536) 0 23406 46811 4681 28087 51493 9362 ;C14_4^5(0..6) 32768 56174 14043 37449 60855 18725 42130 ;C14_4^5(7..13) ph12=(65536) 0 23406 46811 4681 28087 51493 9362 32768 56174 14043 37449 60855 18725 42130 ph13=(65536) 0 23406 46811 4681 28087 51493 9362 32768 56174 14043 37449 60855 18725 42130 ph14=(65536) 0 23406 46811 4681 28087 51493 9362 32768 56174 14043 37449 60855 18725 42130 ;;C14_4^5 excitation and reconversion pulse phases ;are identical ph5= 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 ph31 = 0 2 0 2 2 0 2 0 1 3 1 3 3 1 3 1 ;ph31 = ph5 + 2*ph13