The page you are about to view requires (1) Internet Explorer 6+ and MathPlayer, or Netscape7/Mozilla/Firefox and MathML fonts for the mathematical formulae using MathML 2.0; (2) Internet Explorer 6+ and Adobe SVG Viewer for vector graphics using SVG 1.1.
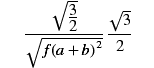
|
If the two examples above are mathematically the same, your browser is correctly displaying MathML.
Quadrupole interaction in high magnetic field
The first two terms in the Magnus expansion of the quadrupole
interaction are:
(1) the first-order quadrupole interaction
(一階四極矩作用力),
and (2) the second-order quadrupole interaction
(二階四極矩作用力),
with
where
are the spherical components of the second-rank EFG tensor.
In its principal-axis system, the components of this tensor are:
The direct products of the EFG second-rank irreducible
tensors can be expressed as higher rank spherical tensors
W using the Clebsch-Gordan coefficients. Since
and
,
we simply have
where
.
The second-order quadrupole interaction becomes:
The eigen values of the fourth-rank EFG tensor W in the spherical tensor representation are:
References
- Wikipedia: Table of Clebsch–Gordan coefficients
- Wikipedia: Wigner 3-j symbols
- Wolfram MathWorld: Wigner 3j-symbol
- Clebsch-Gordon or Wigner 3j coefficients for coupling angular momentum
- Anthony Stone's Wigner coefficient calculator
- Particle Data Group: Clebsch-Gordan coefficients (PDF file)
- SO(3) Clebsch Gordan coefficients
- Wikipedia: Table of spherical harmonics
(top)
